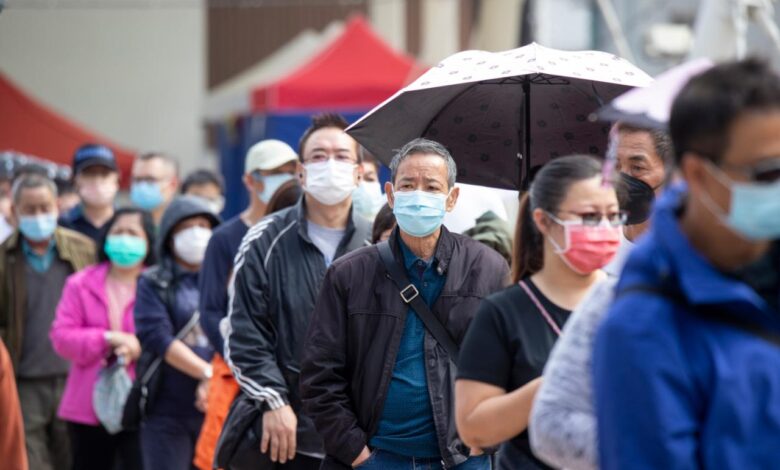
Some Cities Could Return to Indoor Masking: What You Need to Know
Some cities could return to indoor masking heres what you need to know – Some cities could return to indoor masking: what you need to know. With COVID-19 cases on the rise again, many are wondering if we’re headed back to those days of masks and social distancing. The emergence of new variants and the potential for another wave of infections has prompted some cities to consider reinstating indoor mask mandates.
But before you start stocking up on face coverings, it’s important to understand the latest developments and what they mean for you.
This blog post will explore the reasons behind the potential return of indoor masking, the impact it could have on individuals and businesses, and the alternative measures cities are considering. We’ll also delve into public perception and the future outlook for masking policies.
So, let’s dive into the facts and figure out what this means for us all.
Rising COVID-19 Cases and Indoor Masking
A resurgence of COVID-19 cases across several cities has led to renewed concerns about the virus’s impact. The rise in cases has prompted discussions about the potential return of indoor masking mandates in some areas.
Factors Contributing to the Surge in Cases
The recent surge in COVID-19 cases can be attributed to a combination of factors. One key factor is the emergence of new variants, such as the Omicron subvariants, which are more transmissible and can evade existing immunity. The waning effectiveness of vaccines over time, particularly against infection, also plays a role.
Additionally, the relaxation of public health measures, such as mask mandates and social distancing guidelines, has contributed to the increased spread of the virus.
Impact of Indoor Masking on Individuals and Businesses: Some Cities Could Return To Indoor Masking Heres What You Need To Know

The return of indoor masking in some cities has sparked debate about its impact on individuals and businesses. While the primary goal of masking is to curb the spread of COVID-19, it’s important to consider the multifaceted implications of this measure.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Indoor Masking for Individuals
Indoor masking can provide individuals with a layer of protection against respiratory illnesses, including COVID-19. Masks act as a physical barrier, reducing the transmission of respiratory droplets. This is particularly important in enclosed spaces where ventilation may be limited.
- Reduced risk of infection:Studies have shown that masks can significantly reduce the transmission of respiratory viruses, including COVID-19. A study published in the journal “Nature” found that wearing a surgical mask reduced the risk of infection by 65% compared to not wearing a mask.
- Protection for vulnerable individuals:Masks are especially important for protecting individuals who are at higher risk of severe illness from COVID-19, such as older adults and people with underlying health conditions.
- Peace of mind:For some individuals, wearing a mask can provide a sense of security and peace of mind, knowing that they are taking steps to protect themselves and others.
However, indoor masking can also have some drawbacks for individuals.
- Discomfort:Wearing a mask for extended periods can be uncomfortable, especially in hot or humid environments.
- Difficulty breathing:Some individuals may find it difficult to breathe while wearing a mask, particularly those with respiratory conditions.
- Communication challenges:Masks can make it difficult to communicate clearly, especially for people who rely on lip reading or facial expressions.
- Mental health:For some individuals, wearing a mask can trigger feelings of anxiety or claustrophobia.
Economic Impact of Indoor Masking on Businesses, Some cities could return to indoor masking heres what you need to know
The economic impact of indoor masking on businesses is complex and multifaceted. While masking can help to prevent the spread of COVID-19 and minimize disruptions to business operations, it can also lead to challenges and costs.
With some cities potentially returning to indoor masking, it’s a reminder that public health measures can be controversial. The debate often hinges on the balance between individual liberty and collective well-being, a theme explored in this thought-provoking article, free speech is essential for democracy could it also be democracy’s downfall.
Ultimately, navigating these complex issues requires open dialogue and a commitment to finding solutions that protect both individual rights and public health.
- Reduced customer traffic:Some customers may be reluctant to visit businesses that require indoor masking, potentially leading to a decrease in sales.
- Increased operational costs:Businesses may need to invest in additional supplies, such as masks and hand sanitizer, and implement procedures to ensure compliance with masking requirements.
- Staffing challenges:Some employees may be hesitant to work in environments where masking is required, potentially leading to staffing shortages.
Effectiveness of Different Types of Masks
The effectiveness of different types of masks varies depending on their design, material, and fit.
- Surgical masks:These masks are typically made of multiple layers of non-woven fabric and are designed to filter out large respiratory droplets.
- Cloth masks:These masks are made from various fabrics and can provide some protection, but they are generally less effective than surgical masks or respirators.
- N95 respirators:These masks are designed to filter out at least 95% of airborne particles, including small viruses. They are considered the most effective type of mask for protecting against COVID-19.
It is important to note that the effectiveness of any mask is also dependent on how it is worn and the level of protection required. A well-fitting mask worn consistently can provide significant protection against respiratory illnesses.
With some cities potentially returning to indoor masking, it’s a good time to remember what truly matters. As science says the more of this you give the happier youll be hint its not money , prioritizing your well-being and finding joy in simple things can help navigate any challenges, even if it means wearing a mask again.
Staying informed about public health recommendations and taking necessary precautions is key, but remember, happiness comes from within.
Public Health Guidelines and Recommendations
Public health guidelines regarding indoor masking are constantly evolving based on the latest scientific evidence and the prevalence of COVID-19 in a given area. Health authorities carefully consider various factors when making recommendations, aiming to balance the need for public health protection with the desire to minimize disruptions to daily life.
Factors Considered in Making Recommendations
Health authorities consider several factors when determining indoor masking recommendations, including:
- COVID-19 Transmission Rates:The level of community transmission is a primary consideration. High transmission rates often warrant stronger recommendations, such as universal indoor masking.
- Hospitalization Rates:The number of COVID-19 patients hospitalized is another key indicator. Increasing hospitalization rates can signal a strain on healthcare systems and might prompt stricter masking guidance.
- Vaccination Rates:Vaccination coverage significantly impacts the severity of outbreaks. Higher vaccination rates generally correlate with lower transmission and hospitalization rates, potentially leading to less stringent masking recommendations.
- Variant Prevalence:The emergence of new variants with increased transmissibility or immune evasion can necessitate adjustments to masking guidelines.
- Local Context:Factors specific to a region, such as population density, healthcare capacity, and community vulnerability, are also considered.
CDC’s Recommendations on Indoor Masking
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides guidance on indoor masking based on community transmission levels. The CDC’s recommendations are as follows:
- High Community Transmission:The CDC recommends wearing a mask indoors, regardless of vaccination status. This applies to individuals who are at increased risk for severe COVID-19, such as older adults and those with underlying medical conditions.
- Medium or Low Community Transmission:In areas with medium or low transmission levels, the CDC recommends that individuals who are unvaccinated, not fully vaccinated, or at increased risk for severe COVID-19 wear a mask indoors.
- Individuals with Symptoms:The CDC recommends that everyone wear a mask indoors if they have symptoms of COVID-19.
- Individuals with a Positive Test:The CDC recommends that individuals with a positive COVID-19 test isolate and wear a mask for at least 5 days after their positive test.
Alternative Measures to Reduce Transmission
As cities grapple with the resurgence of COVID-19, many are exploring alternative measures to mitigate the spread beyond simply requiring indoor masking. These strategies aim to reduce transmission while minimizing disruptions to daily life and business operations.
Effectiveness of Alternative Measures
While masking remains a highly effective strategy for preventing the spread of respiratory droplets, alternative measures can play a complementary role in reducing transmission. These measures, such as improved ventilation, air filtration, and increased testing, can create a layered approach to reducing the risk of COVID-19 spread.
Examples of Alternative Measures Implemented by Cities
- Improved Ventilation:Cities like New York City have implemented mandates for businesses to improve ventilation systems, ensuring adequate airflow and reducing the concentration of airborne viruses.
- Air Filtration:Some cities, such as Los Angeles, have encouraged the use of high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters in indoor spaces, particularly in schools and public transportation. These filters can effectively remove airborne particles, including virus-laden droplets.
- Increased Testing:Cities like San Francisco have expanded access to free COVID-19 testing, encouraging regular testing, especially for individuals with symptoms or those who have been exposed to the virus. This helps identify positive cases early and facilitate isolation, limiting further transmission.
Public Perception and Response
The return of indoor masking mandates is a complex issue, often met with a mix of emotions and opinions. Public perception and response to such measures can vary widely, influenced by a multitude of factors.
Public Opinion on the Return of Indoor Masking Mandates
Public opinion on the return of indoor masking mandates is often polarized, with differing viewpoints stemming from concerns about individual liberty, the effectiveness of masking, and the perceived threat of COVID-19.
It’s crazy how things are changing so fast. One minute we’re talking about cities potentially returning to indoor masking, the next we’re discussing the geopolitical implications of a possible Pelosi trip to Taiwan, a move that could test China’s appetite for confrontation.
It’s a reminder that even as we navigate the complexities of public health, global events can quickly shift our focus to larger, more volatile matters. While masks might be back on the table in some places, it’s clear that the world is a place of constant flux, and we need to be prepared for whatever comes next.
- Some individuals may express strong support for masking mandates, citing the need to protect public health and prevent the spread of the virus, especially among vulnerable populations.
- Others may oppose mandates, arguing that they infringe on personal freedoms, citing potential economic and social consequences, or questioning the scientific evidence supporting their effectiveness.
- Public opinion can also be influenced by political affiliation, with some studies suggesting a correlation between political leanings and attitudes towards masking.
Potential for Public Resistance or Compliance
The potential for public resistance or compliance with indoor masking mandates depends on various factors, including the severity of the pandemic, public trust in authorities, and the perceived effectiveness of the mandates.
- In situations where COVID-19 cases are rising rapidly and hospitalizations are increasing, public compliance with masking mandates may be higher, driven by a sense of urgency and concern for public health.
- Conversely, if the pandemic is perceived as less severe, or if there is a lack of trust in government or public health officials, resistance to mandates may be more prevalent.
- The implementation of mandates, including clear communication, enforcement strategies, and the provision of resources such as masks, can also influence public compliance.
Factors Influencing Public Perception of Indoor Masking
Public perception of indoor masking is influenced by a range of factors, including:
- Personal Experiences:Individuals who have experienced COVID-19 firsthand or have close friends or family members who have been affected may be more likely to support masking mandates.
- Trust in Authorities:Public trust in government and public health officials is a key factor influencing public perception of masking. If there is a lack of trust, people may be less likely to comply with mandates.
- Media Coverage:Media coverage can significantly shape public opinion on masking, with conflicting reports and narratives potentially contributing to confusion and skepticism.
- Social Norms:Social norms and peer pressure can influence individual behavior, with people more likely to comply with masking mandates if they see others doing so.
- Economic Considerations:The economic impact of masking mandates, such as potential business closures or disruptions, can also influence public opinion, with some individuals prioritizing economic concerns over public health.
Future Outlook and Predictions
Predicting the future of indoor masking is a complex task, as it depends on a multitude of factors, including the evolution of the virus, public health guidelines, and societal attitudes. While it is impossible to say with certainty what the future holds, analyzing current trends and expert opinions can help us formulate potential scenarios and understand the key factors influencing future decisions.
Potential Scenarios for the Future of Indoor Masking
The future of indoor masking is likely to be dynamic, with periods of increased masking followed by periods of relaxation, depending on the prevailing circumstances. Here’s a possible timeline outlining potential scenarios:
- Short Term (Next 6-12 Months):In the short term, indoor masking may continue to be recommended or even mandated in certain settings, especially in areas with high transmission rates or vulnerable populations. The emergence of new variants, particularly those with increased transmissibility or immune evasion capabilities, could lead to a resurgence of masking recommendations.
- Mid-Term (1-3 Years):As the pandemic transitions into an endemic phase, indoor masking may become less frequent and more targeted. Masking recommendations could be tailored to specific risk groups, such as the elderly or immunocompromised, or situations with high density and prolonged exposure.
- Long Term (Beyond 3 Years):In the long term, indoor masking could become a seasonal or situational practice, similar to how we use flu masks during peak season. The need for masking may be determined by the emergence of new variants, the effectiveness of existing vaccines and treatments, and the overall level of immunity within the population.
Impact of Future COVID-19 Variants on Masking Policies
The emergence of new COVID-19 variants with enhanced transmissibility or immune evasion capabilities could significantly impact masking policies. Variants like Omicron have demonstrated the potential to rapidly spread and evade existing immunity, leading to a resurgence of cases and renewed calls for masking.
- Increased Transmissibility:Variants with higher transmissibility, like Omicron, can lead to more rapid spread and increased case numbers, potentially overwhelming healthcare systems and requiring stricter mitigation measures, including indoor masking.
- Immune Evasion:Variants capable of evading existing immunity, either from vaccines or prior infection, could lead to breakthrough infections and require renewed focus on masking, particularly among vulnerable populations.
- Severity of Illness:While future variants might be more transmissible, they may not necessarily lead to more severe illness. However, if a new variant causes more severe disease, it could lead to increased hospitalization rates and necessitate stricter mitigation measures, including masking.
Key Factors Influencing Future Decisions Regarding Indoor Masking
Numerous factors will influence future decisions regarding indoor masking, including:
| Factor | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| COVID-19 Transmission Rates | High transmission rates, as seen with the Omicron variant, often lead to renewed calls for masking. | A surge in COVID-19 cases in a particular region could prompt local authorities to reinstate indoor masking mandates. |
| Hospitalization Rates | Increased hospitalization rates, particularly among vulnerable populations, can trigger stricter mitigation measures, including masking. | If a new variant leads to a significant increase in hospitalizations, it could prompt a return to widespread indoor masking. |
| Vaccination Rates | High vaccination rates can reduce the severity of COVID-19 and lower the risk of transmission, potentially leading to a relaxation of masking policies. | Regions with high vaccination rates may be able to ease masking restrictions sooner than those with lower vaccination rates. |
| Public Health Guidance | Recommendations from public health agencies, such as the CDC or WHO, will continue to play a significant role in shaping masking policies. | Updated guidelines from the CDC recommending indoor masking in certain settings could influence local authorities to implement similar policies. |
| Public Acceptance and Compliance | The level of public acceptance and compliance with masking policies will influence their effectiveness and longevity. | If there is widespread resistance to masking mandates, they may be less effective and harder to enforce. |
Final Thoughts
The potential return of indoor masking is a complex issue with no easy answers. While it’s important to be prepared for the possibility of a resurgence in COVID-19 cases, it’s also crucial to stay informed about the latest developments and recommendations from public health officials.
By understanding the factors at play and the potential consequences, we can navigate this challenging situation with greater awareness and preparedness. Ultimately, our collective efforts to protect ourselves and our communities will determine the course of this pandemic.