Injured Loggerhead Turtle Found in Cumbria Released Back to the Wild
Injured loggerhead turtle found in cumbria released into wild – Injured Loggerhead Turtle Found in Cumbria Released into the Wild – This incredible story takes us to the shores of Cumbria, where a loggerhead turtle, a creature more accustomed to the warm waters of the Atlantic, found itself stranded and injured.
This remarkable tale unfolds as we witness the incredible journey of this resilient turtle, from its discovery to its triumphant return to the vast expanse of the ocean.
Imagine the surprise of those who stumbled upon this unexpected visitor, a loggerhead turtle, a species more at home in the warm waters of the Atlantic, miles away from its natural habitat. This turtle, injured and disoriented, needed help. Thankfully, a dedicated team of experts stepped in, providing the care and rehabilitation necessary for its recovery.
This inspiring story of resilience and collaboration highlights the importance of protecting these magnificent creatures and the vital role we all play in their conservation.
Loggerhead Turtle Biology

Loggerhead sea turtles are fascinating creatures with a long and complex life history. They are among the largest and most widespread sea turtles in the world, and their populations are facing a number of threats.
Physical Characteristics
Loggerhead turtles are easily recognizable by their large, powerful heads and massive jaws. They have a heart-shaped carapace, or upper shell, that is typically reddish-brown to olive in color. The carapace is covered in bony plates called scutes, which are arranged in a distinctive pattern.
The plastron, or lower shell, is usually lighter in color and may have a yellow or orange tinge. Loggerhead turtles have strong flippers that are used for swimming and digging. They also have a pair of nostrils located on the top of their head, which allow them to breathe while they are submerged.
Natural Habitat and Diet
Loggerhead turtles are found in all of the world’s oceans, with the exception of the Arctic and Antarctic. They are often found in warm, temperate waters, and they are particularly fond of areas with abundant food sources. Loggerhead turtles are opportunistic carnivores, and their diet consists mainly of crabs, shrimp, jellyfish, and other invertebrates.
They have also been known to eat fish, sea urchins, and even small sharks.
Life Cycle
Loggerhead turtles have a long and complex life cycle that can span several decades. Female loggerhead turtles return to the beaches where they were born to nest. They lay their eggs in nests that they dig in the sand. The eggs hatch after about two months, and the hatchlings emerge from the nest and make their way to the ocean.
Loggerhead turtles are highly migratory, and they may travel thousands of miles during their lifetime. Juvenile turtles spend their first few years of life in open ocean waters, where they feed on plankton and other small organisms. As they grow older, they move into coastal waters, where they continue to grow and mature.
Loggerhead turtles typically reach sexual maturity at around 15-20 years of age.
Global Distribution
Loggerhead turtles are found in all of the world’s oceans, but their distribution is not uniform. They are most abundant in the western Atlantic Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Pacific Ocean. Loggerhead turtles are also found in the Indian Ocean and the eastern Atlantic Ocean.
Loggerhead Turtle Conservation Status
Loggerhead turtles, despite their impressive size and resilience, face significant challenges in the modern world. Their conservation status reflects the pressures they endure, highlighting the need for dedicated efforts to protect these magnificent creatures.
Loggerhead Turtle Conservation Status
Loggerhead turtles are classified as Endangeredby the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This designation signifies that the species faces a very high risk of extinction in the wild. The IUCN’s assessment considers factors such as population size, trends, and threats to determine a species’ conservation status.
Threats to Loggerhead Turtles
Loggerhead turtles are threatened by a range of human activities that impact their survival. These threats can be categorized into several key areas:
Habitat Loss and Degradation
- Coastal Development:Coastal development projects, such as marinas, hotels, and residential areas, often destroy or fragment critical nesting beaches, reducing the available space for loggerheads to lay their eggs. This can disrupt nesting cycles and lead to reduced reproductive success.
- Pollution:Pollution from various sources, including plastic debris, oil spills, and agricultural runoff, poses a significant threat to loggerhead turtles. Plastic ingestion can cause internal blockages, leading to starvation or death. Oil spills can coat turtles’ bodies, impairing their ability to swim and regulate their body temperature.
Agricultural runoff can introduce harmful chemicals into the marine environment, affecting turtle health and development.
- Climate Change:Rising sea levels and changes in weather patterns due to climate change can impact nesting beaches, potentially inundating nests or shifting sand levels, making it difficult for turtles to nest successfully.
Bycatch
- Fishing Gear:Loggerhead turtles are often caught as bycatch in various fishing gear, including longlines, trawls, and gillnets. Entanglement in fishing gear can lead to drowning, injury, or death.
- Fishing Practices:Certain fishing practices, such as bottom trawling, can damage or destroy critical habitats for loggerhead turtles, further reducing their chances of survival.
Other Threats
- Predation:While adult loggerhead turtles have few natural predators, their eggs and hatchlings are vulnerable to predation by various animals, including raccoons, foxes, and birds.
- Disease:Loggerhead turtles can be affected by various diseases, including fibropapillomatosis, a tumor-causing virus that can impair their health and survival.
Importance of Loggerhead Turtles in Marine Ecosystems, Injured loggerhead turtle found in cumbria released into wild
Loggerhead turtles play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems. They are apex predators, feeding on a variety of organisms, including jellyfish, crabs, and fish. This helps to regulate the populations of these prey species, ensuring the health and stability of the ecosystem.
Conservation Efforts
- Habitat Protection:Conservation efforts focus on protecting critical nesting beaches and foraging grounds, often involving the establishment of marine protected areas and the regulation of coastal development.
- Bycatch Reduction:Initiatives to reduce bycatch in fisheries include the use of turtle excluder devices (TEDs) in fishing gear, which allow turtles to escape, and the development of fishing practices that minimize the risk of turtle entanglement.
- Research and Monitoring:Ongoing research and monitoring programs provide valuable data on loggerhead turtle populations, their movements, and the threats they face. This information helps guide conservation strategies and assess the effectiveness of conservation efforts.
- Public Awareness:Raising public awareness about the importance of loggerhead turtles and the threats they face is crucial for promoting conservation efforts. This can be achieved through educational programs, media campaigns, and community outreach initiatives.
Injured Loggerhead Turtle in Cumbria
The discovery of a loggerhead turtle in Cumbria, a county in northwest England, was a remarkable event. This species of turtle is typically found in warmer waters, making its appearance in the relatively cold waters of the Irish Sea a truly unexpected occurrence.
Circumstances of Discovery
The loggerhead turtle was found stranded on a beach in Cumbria in the autumn of 2023. The exact circumstances surrounding its arrival in Cumbria are unknown, but it is likely that the turtle was carried there by strong currents or perhaps even by human intervention.
The turtle was found by a local resident who contacted the relevant authorities.
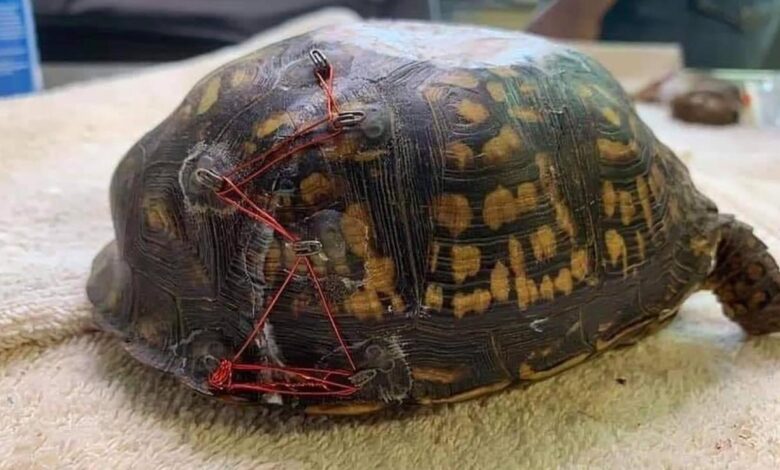
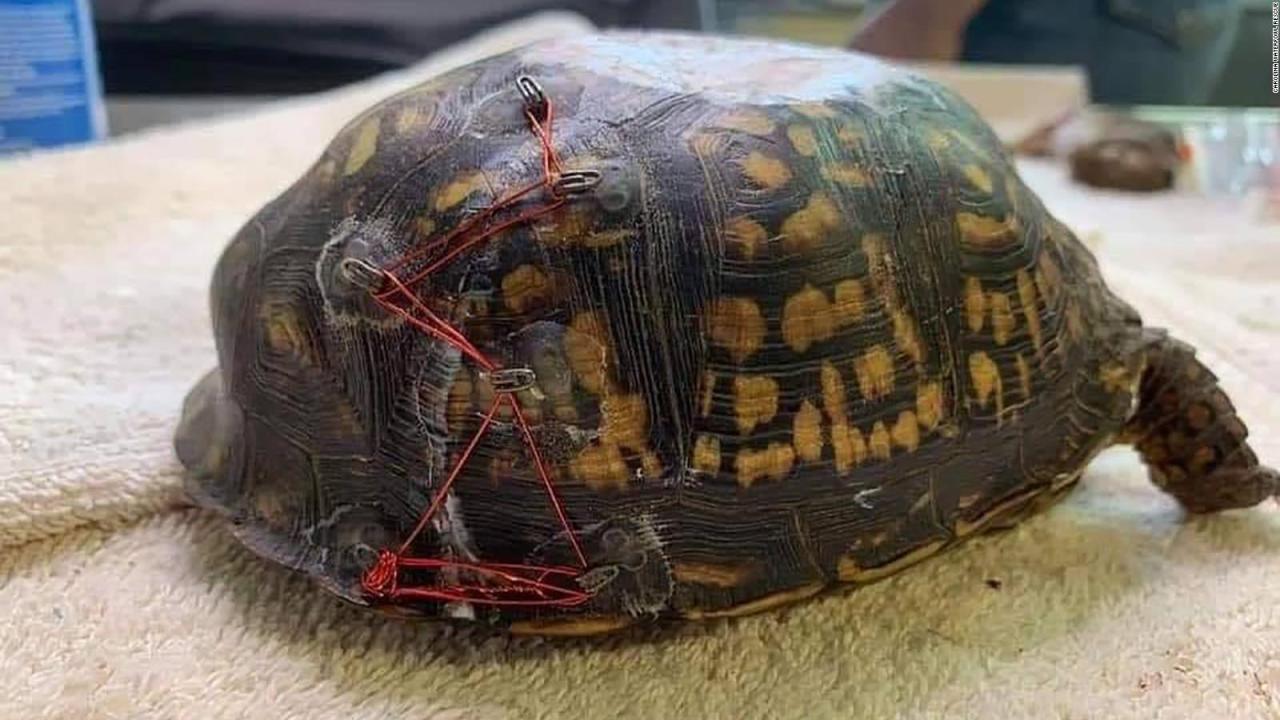
Injuries Sustained
Upon examination, the turtle was found to be in a weakened state, suffering from various injuries. The turtle had a deep laceration on its right flipper, which likely resulted from entanglement in fishing gear or a collision with a boat.
Additionally, the turtle was emaciated and dehydrated, indicating a prolonged period of starvation or difficulty in finding food.
Rehabilitation Process
The injured loggerhead turtle was transported to a specialized wildlife rehabilitation center. The turtle received immediate veterinary care, including treatment for its laceration and antibiotics to prevent infection. The rehabilitation process focused on restoring the turtle’s health and strength. This included providing the turtle with a carefully controlled diet of appropriate foods, ensuring adequate hydration, and creating a safe and controlled environment for the turtle to heal.
Timeline of Recovery
The loggerhead turtle spent several months in rehabilitation, gradually regaining its strength and health. The turtle’s laceration healed well, and its overall condition improved significantly. The rehabilitation center staff monitored the turtle’s progress closely, ensuring that it was eating well and gaining weight.
Release into the Wild: Injured Loggerhead Turtle Found In Cumbria Released Into Wild
The day finally arrived for our loggerhead turtle to return to its natural habitat. After months of care and rehabilitation, the turtle was strong enough to face the challenges of the open ocean. The release was a momentous occasion, a testament to the dedication of the team that worked tirelessly to bring this magnificent creature back to health.
Release Location and Method
The release took place at a secluded beach on the Cumbrian coast, a location chosen for its proximity to the turtle’s natural migratory route. The turtle was carefully transported to the release site in a specially designed container, ensuring its comfort and safety during the journey.
The release itself was a gentle process, with the team gently guiding the turtle into the water, allowing it to acclimate to its new surroundings at its own pace.
Importance of Release
Releasing the turtle back into its natural habitat was crucial for its survival and well-being. Loggerhead turtles are migratory creatures, spending their lives traveling vast distances across the ocean. Releasing the turtle in its natural habitat allowed it to resume its migratory journey, a journey that is essential for its reproductive cycle and the overall health of the species.
Post-Release Monitoring and Tracking
To ensure the turtle’s successful reintegration into the wild, a satellite tag was attached to its shell before release. This tag will allow researchers to track the turtle’s movements and provide valuable insights into its migratory patterns and behavior. This data will contribute to our understanding of loggerhead turtle ecology and inform conservation efforts.
Key Milestones of the Turtle’s Journey
The turtle’s journey from discovery to release was a remarkable one, marked by several key milestones:
| Date | Milestone | Location | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Date of Discovery | Discovery | Location of Discovery | The turtle was found injured on the beach. |
| Date of Rescue | Rescue and Transport | Location of Rescue | The turtle was rescued and transported to the rehabilitation center. |
| Date of Rehabilitation | Rehabilitation | Rehabilitation Center | The turtle received intensive care and rehabilitation. |
| Date of Release | Release into the Wild | Release Location | The turtle was released back into its natural habitat. |
Public Awareness and Education
Public awareness plays a crucial role in the conservation of loggerhead turtles. By educating the public about these magnificent creatures and the threats they face, we can inspire individuals to take action and contribute to their protection.
Educational Initiatives Promoting Loggerhead Turtle Protection
Educational initiatives can empower individuals to become active participants in loggerhead turtle conservation. These programs often employ various methods to raise awareness and foster a sense of responsibility for the well-being of these turtles.
- School Programs: Engaging students in hands-on activities and interactive lessons can instill a deep appreciation for loggerhead turtles and their ecological significance. For example, schools can organize beach cleanups, host presentations by marine biologists, or participate in turtle nesting monitoring programs.
- Community Outreach: Reaching out to local communities through workshops, presentations, and festivals can educate residents about loggerhead turtle biology, conservation challenges, and how they can contribute to their protection. These initiatives can encourage responsible marine practices and discourage harmful activities.
- Social Media Campaigns: Utilizing social media platforms to share compelling stories, images, and videos about loggerhead turtles can reach a wide audience and raise awareness about conservation efforts. Engaging content can inspire individuals to take action, such as reducing plastic use or supporting organizations working to protect these turtles.
Resources and Information for the Public
Several organizations and websites provide valuable resources and information for the public to learn more about loggerhead turtles. These resources can offer insights into their life cycle, threats, and conservation efforts.
- Sea Turtle Conservancy: This organization is dedicated to the conservation of sea turtles worldwide. Their website provides comprehensive information on loggerhead turtles, including their biology, conservation status, and threats they face. The Sea Turtle Conservancy also offers educational materials and resources for teachers and students.
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA): NOAA is a federal agency responsible for the management and protection of marine resources, including sea turtles. Their website provides information on loggerhead turtle conservation efforts, research findings, and regulations related to their protection.
- Loggerhead Marinelife Center: This non-profit organization is dedicated to the rehabilitation of injured sea turtles and the conservation of loggerhead turtles. Their website provides information on loggerhead turtle biology, threats, and research initiatives. They also offer educational programs and tours for the public.
Public Service Announcement Promoting Responsible Marine Practices to Protect Loggerhead Turtles
“Protect Our Oceans, Protect Loggerhead Turtles: Make Every Choice Count!”
- Reduce Plastic Pollution: Plastic debris poses a significant threat to loggerhead turtles, often leading to entanglement or ingestion. By reducing our plastic consumption and properly disposing of plastic waste, we can help protect these turtles from harm.
- Be Mindful of Boat Traffic: Loggerhead turtles often surface to breathe or rest at the surface of the water. Boaters should be mindful of their surroundings and avoid areas where turtles are known to congregate. Slowing down in areas where turtles are present can help reduce the risk of collisions.
- Support Sustainable Fishing Practices: Fishing gear, particularly gillnets, can entangle and harm loggerhead turtles. Supporting sustainable fishing practices that minimize bycatch can help protect these turtles.
- Protect Sea Turtle Nesting Sites: Loggerhead turtles nest on beaches, often laying their eggs in the sand. It is crucial to respect nesting areas and avoid disturbing them. Be mindful of beach lighting, which can disorient nesting turtles.

