Population and Feeding the World: A Growing Challenge
Population and feeding the world is a pressing issue that demands our attention. As the global population continues to rise, so does the demand for food, putting immense pressure on our planet’s resources. This complex challenge involves a delicate interplay between population growth, food production, and environmental sustainability.
We must find ways to produce enough food to nourish a growing population while preserving the environment for future generations.
The world faces a daunting task of ensuring food security for all, especially in the face of climate change, resource scarcity, and inequality. From the fields to the dinner table, our food systems are intricately connected to the well-being of our planet and its inhabitants.
Global Population Growth

The global population has been steadily increasing for centuries, and it continues to grow at a significant rate. Understanding the factors driving this growth and its implications for the planet is crucial for addressing the challenges of feeding and sustaining a growing human population.
Current Population and Projections, Population and feeding the world
The current global population stands at over 8 billion people. The United Nations estimates that the population will reach 9.7 billion by 2050 and could exceed 11 billion by the end of the century. These projections are based on various factors, including birth rates, mortality rates, and migration patterns.
Factors Contributing to Population Growth
Birth Rates
The global birth rate has been declining in recent decades, but it remains higher than the death rate, leading to population growth. The decline in birth rates is attributed to factors such as increased access to education and contraception, urbanization, and changing societal norms.
Feeding a growing global population is a complex challenge, requiring innovative solutions and a focus on sustainability. Sometimes, though, even the simplest things can seem daunting, like navigating the bustling London Underground. If you ever find yourself feeling uneasy about someone’s behavior on the tube, it’s good to remember that suspicious behavior on the tube london underground doesn’t necessarily mean something sinister is afoot.
Just like with feeding the world, a little understanding and a lot of communication can go a long way.
However, birth rates vary significantly across regions, with some countries experiencing high birth rates, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa.
Mortality Rates
Improvements in healthcare, sanitation, and nutrition have significantly reduced mortality rates, particularly among children and infants. Advancements in medical technology have also contributed to increased life expectancy. This decrease in mortality rates, combined with relatively high birth rates, has resulted in population growth.
Migration Patterns
Migration patterns play a significant role in population growth. People migrate for various reasons, including economic opportunities, political instability, and natural disasters. Migration can lead to population increases in destination countries, while contributing to population decreases in origin countries.
Implications of Population Growth
Resource Consumption
Population growth exerts pressure on resources such as food, water, and energy. As the population increases, the demand for these resources also rises, leading to potential shortages and competition for limited resources. This is particularly concerning in regions with already strained resources.
Environmental Sustainability
Population growth can have significant environmental impacts. Increased resource consumption leads to deforestation, pollution, and climate change. The growing demand for food and energy contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and habitat loss.
The ever-growing global population poses a significant challenge in ensuring food security for everyone. As resources become scarcer, finding sustainable solutions is paramount. Noam Chomsky, in his insightful analysis of “the world after Sept 11,” chomsky the world after sept 11 , highlights the need for a fundamental shift in our priorities, moving away from militarism and towards addressing issues like climate change and global inequality, both of which have a direct impact on food production and distribution.
“The Earth’s resources are finite, and the human population is growing exponentially. If we continue on our current trajectory, we risk exceeding the carrying capacity of the planet.”Dr. Jane Goodall
Sustainable Food Systems

The global population is expected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, placing immense pressure on our food systems. Feeding this growing population while safeguarding the environment requires a fundamental shift towards sustainable food systems. Sustainable food systems aim to produce enough food to meet current and future needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
They prioritize environmental, social, and economic sustainability, ensuring food security for all while minimizing negative impacts on the planet.
Importance of Sustainable Food Systems
Sustainable food systems are crucial for ensuring food security and environmental sustainability. They contribute to a more resilient and equitable food system by addressing key challenges such as climate change, resource depletion, and social inequality. By adopting sustainable practices, we can protect biodiversity, conserve water resources, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Feeding a growing global population is a complex challenge, requiring innovative solutions and collaborative efforts. Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) play a crucial role in tackling this issue, working on various fronts like promoting sustainable agriculture, improving food distribution systems, and empowering local communities to enhance food security.
Organizations like those featured on this blog are dedicated to finding lasting solutions to ensure that everyone has access to nutritious food. By supporting these NGOs, we can contribute to a more equitable and food-secure future for all.
This approach fosters a more just and equitable food system, promoting fair wages for farmers and workers, and ensuring access to nutritious food for all.
Sustainable Agricultural Practices
Sustainable agriculture involves a range of practices that promote food security and environmental conservation. These practices minimize environmental impact, conserve natural resources, and enhance biodiversity. Some examples of sustainable agricultural practices include:
- Agroecology: This approach integrates ecological principles into farming practices, focusing on biodiversity, natural pest control, and soil health. It emphasizes the use of organic fertilizers, crop rotation, and intercropping to enhance soil fertility and reduce reliance on synthetic inputs.
- Conservation Agriculture: This practice minimizes soil disturbance, maintains permanent soil cover, and promotes crop diversity. It helps reduce erosion, improve soil health, and enhance water retention, leading to increased yields and reduced reliance on fertilizers and pesticides.
- Organic Farming: Organic farming prohibits the use of synthetic pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers. It emphasizes the use of natural inputs, such as compost and manure, to improve soil fertility and promote biodiversity. Organic farming contributes to environmental protection and human health by reducing chemical residues in food and the environment.
- Precision Agriculture: This technology-driven approach uses sensors, data analysis, and automation to optimize resource use and improve crop yields. By monitoring soil conditions, weather patterns, and plant growth, farmers can apply precise amounts of water, fertilizer, and pesticides, minimizing waste and environmental impact.
Role of Technology and Innovation
Technology and innovation play a vital role in improving food production and distribution, contributing to the development of sustainable food systems.
- Vertical Farming: This innovative approach involves growing crops in stacked layers, maximizing space and resource efficiency. Vertical farms can be located in urban areas, reducing transportation distances and minimizing environmental impact. They also offer greater control over growing conditions, enabling year-round production and reduced water consumption.
- Gene Editing: Gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR-Cas9, allow scientists to modify crops for improved yields, nutritional content, and resistance to pests and diseases. This can enhance food security and reduce the need for chemical inputs, contributing to a more sustainable food system.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology can enhance food traceability, transparency, and accountability. By tracking food products from farm to table, blockchain can improve food safety, reduce fraud, and empower consumers to make informed choices about their food.
Food Security and Nutrition: Population And Feeding The World
Food security is a fundamental human right and a crucial component of sustainable development. It encompasses the ability of individuals and populations to access, utilize, and have a stable supply of safe, nutritious food that meets their dietary needs and preferences for an active and healthy life.
Key Components of Food Security
Food security is a multifaceted concept that encompasses four key components:
- Availability: This refers to the physical presence of food in sufficient quantities at the local level. It involves factors such as food production, imports, and distribution systems.
- Access: This component focuses on the ability of individuals to acquire adequate food, whether through purchase, production, or other means. It considers factors such as income, market prices, and social safety nets.
- Utilization: This aspect refers to the ability of individuals to consume food and utilize the nutrients from it to meet their nutritional needs. It involves factors such as knowledge about healthy diets, food preparation practices, and the presence of diseases that may hinder nutrient absorption.
- Stability: This component refers to the consistent availability of food over time, ensuring that people have access to food during periods of crisis, such as natural disasters or economic shocks.
Challenges to Food Security
Several factors can undermine food security, leading to food insecurity and malnutrition. These challenges include:
- Poverty: Poverty is a significant driver of food insecurity, as it limits people’s ability to afford adequate food.
- Inequality: Inequality in income, access to resources, and social status can exacerbate food insecurity, disproportionately affecting vulnerable groups, such as women, children, and marginalized communities.
- Conflict: Armed conflict can disrupt food production, distribution, and access, leading to widespread food insecurity and malnutrition.
- Climate Change: Climate change can have severe impacts on agricultural production, leading to crop failures, water scarcity, and increased food prices, further exacerbating food insecurity.
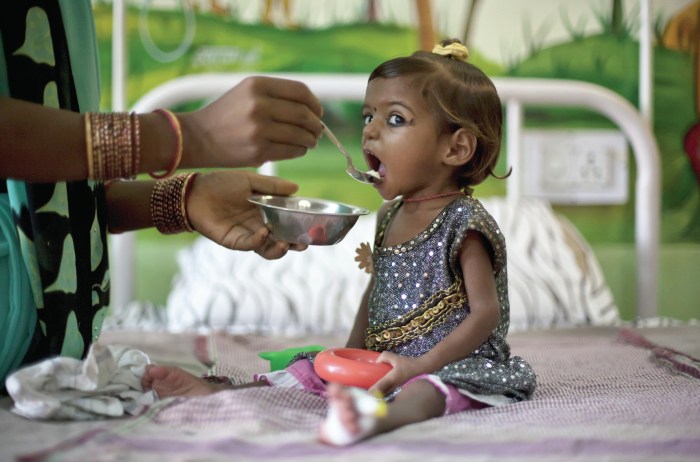
Impact of Malnutrition
Malnutrition, which includes both undernutrition and overnutrition, has profound and far-reaching consequences for individuals and societies.
- Undernutrition: Undernutrition, which encompasses stunting, wasting, and micronutrient deficiencies, can lead to impaired physical and cognitive development, increased susceptibility to infections, and higher mortality rates, particularly among children.
- Overnutrition: Overnutrition, characterized by excessive consumption of calories and unhealthy fats, can lead to obesity, chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease, and increased healthcare costs.
Consumer Choices and Responsibility
The choices we make as consumers have a profound impact on the food system, influencing everything from farm practices to environmental sustainability. By making conscious decisions about what we eat and how we consume, we can contribute to building a more equitable and sustainable food system.
The Power of Consumer Choices
Consumers have the power to shape the food system by choosing products that align with their values and priorities. When consumers prioritize sustainability, they send a strong message to producers and retailers to adopt more environmentally friendly practices. This can include choosing organic produce, supporting local farmers, and reducing food waste.
Responsible Food Consumption Practices
Reducing Food Waste
Food waste is a significant problem globally, contributing to environmental degradation and food insecurity. Consumers can play a crucial role in reducing food waste by adopting simple practices:
- Plan meals in advance to avoid buying excess food.
- Store food properly to extend its shelf life.
- Use leftovers creatively in new dishes.
- Compost food scraps to reduce landfill waste.
Supporting Local Farmers
Supporting local farmers contributes to building a more resilient and sustainable food system. By purchasing directly from farmers’ markets or subscribing to Community Supported Agriculture (CSA) programs, consumers can ensure that their food is locally sourced and produced with environmentally friendly practices.
Choosing Sustainable Products
Consumers can also make a difference by choosing sustainable food products. This includes looking for certifications such as Fair Trade, Organic, and Rainforest Alliance, which indicate that products are produced with ethical and sustainable practices.
Individual Actions for Food Security and Environmental Sustainability
Consumers can take individual actions to promote food security and environmental sustainability:
- Reduce meat consumption: Animal agriculture is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions and deforestation. Reducing meat consumption can help reduce environmental impact.
- Support sustainable food initiatives: Engage with organizations promoting food security and sustainable food systems.
- Educate others: Share information about sustainable food practices with family, friends, and community members.