
Climate Change Affects Biodiversity: A Looming Threat
Climate change affects biodiversity in profound ways, disrupting ecosystems and threatening the delicate balance of life on Earth. Rising global temperatures are causing shifts in species distribution, altering habitats, and pushing many species towards extinction. The consequences of this loss are far-reaching, impacting everything from food security to disease control.
From the bleaching of coral reefs to the shrinking of glaciers, climate change is leaving its mark on every corner of the planet. This shift in the Earth’s climate is altering the very foundation of life, threatening the biodiversity that sustains us all.
The impact on biodiversity is not just an environmental concern; it’s a matter of survival for humanity.
The Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity

The Earth’s biodiversity is facing an unprecedented threat from climate change. Rising global temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events are disrupting ecosystems and pushing species to their limits. These changes are impacting species distribution, habitat suitability, and ultimately, the very survival of countless life forms.
Climate change is a serious threat to biodiversity, causing habitat loss, shifting species ranges, and disrupting ecosystems. The United Nations plays a crucial role in addressing these issues, focusing on sustainable development and promoting international cooperation to combat climate change, as seen on their website united nations on development issues.
By working together, we can protect our planet’s biodiversity and ensure a sustainable future for all.
Species Distribution and Habitat Suitability
Climate change is altering the distribution of species across the globe. As temperatures rise and precipitation patterns shift, species are forced to move to new areas in search of suitable habitats. This can lead to range shifts, where species expand or contract their geographic distribution.
For example, some bird species are shifting their breeding ranges northward as temperatures increase. However, this migration can be challenging, especially for species that are already facing habitat loss or fragmentation.
The interconnectedness of life on Earth is truly remarkable. Climate change disrupts this delicate balance, pushing species to the brink and altering ecosystems forever. It’s a complex issue, and sometimes it feels like we’re fighting a losing battle. I recently wrote about why I opposed the resolution to authorize force, a decision that weighed heavily on my conscience , because I believe that peaceful solutions are crucial in addressing global challenges.
Ultimately, we need to find ways to work together, across borders and ideologies, to protect our planet and ensure a future where biodiversity thrives.
- Rising temperatures can lead to the loss of suitable habitat for species that are adapted to specific temperature ranges. For example, the American pika, a small mammal found in high-altitude regions, is facing a decline in population due to warming temperatures.
As temperatures increase, pikas are forced to move to higher elevations, but their range is limited by the availability of suitable habitat.
- Changes in precipitation patterns can also have a significant impact on species distribution. For instance, the African savanna is experiencing increased drought due to climate change. This is leading to a decline in the populations of herbivores like zebras and wildebeest, which rely on grasslands for food and water.
Climate change is a silent, insidious force, impacting ecosystems in ways we’re only beginning to understand. It’s not just about rising temperatures; it’s about shifting weather patterns, altered habitats, and the disruption of delicate balances within nature. Think of it as a new kind of empire, reaching the parts other empires could not reach , but instead of conquest, it brings disruption and decay.
This unseen empire is slowly dismantling the intricate web of life, leaving behind a world less vibrant and less resilient.
- Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, and wildfires, can cause widespread habitat destruction and mortality. These events can disrupt ecological processes and alter the composition of communities.
Vulnerable Species and Specific Threats
Many species are particularly vulnerable to climate change. These species are often found in geographically restricted areas, have specialized ecological requirements, or are already facing other threats, such as habitat loss or overexploitation.
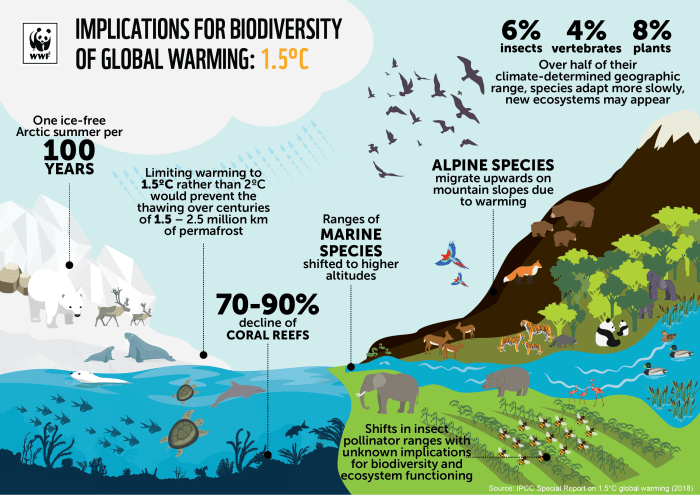
- Coral reefs are highly sensitive to ocean warming and acidification. As ocean temperatures rise, corals expel the algae that provide them with food and color, leading to coral bleaching. This phenomenon can cause widespread coral death and threaten the entire reef ecosystem.
- Polar bears are highly adapted to the Arctic environment, relying on sea ice for hunting seals. As sea ice melts due to climate change, polar bears are losing access to their primary food source. This is leading to declines in their populations and increased competition for food.
- Amphibians are particularly vulnerable to climate change because they have permeable skin that is susceptible to changes in temperature and humidity. Climate change is also altering the timing of breeding seasons, which can disrupt amphibian life cycles.
Consequences of Species Extinction and Loss of Biodiversity
The extinction of species and the loss of biodiversity have profound consequences for ecosystems and human well-being.
- Loss of biodiversity can disrupt ecosystem functions, such as pollination, pest control, and water purification. These services are essential for human survival and well-being.
- Species extinction can lead to a cascade effect, where the loss of one species triggers the decline of other species that depend on it. This can create a domino effect, destabilizing entire ecosystems.
- Loss of biodiversity can also have economic consequences, as species provide valuable resources, such as food, medicine, and building materials.
Climate Change and Ecosystem Services: Climate Change Affects Biodiversity
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in providing essential ecosystem services that underpin human well-being. These services include pollination, water purification, and carbon sequestration, all of which are vital for maintaining a healthy planet and supporting human societies. Climate change poses a significant threat to these services, potentially leading to cascading effects on human livelihoods and the global economy.
The Impact of Climate Change on Ecosystem Services
Climate change is altering the delicate balance of ecosystems, impacting their ability to provide vital services. Rising temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events are disrupting natural processes, leading to shifts in species distributions, changes in plant and animal communities, and increased vulnerability to invasive species and disease outbreaks.
Pollination
Pollination is a crucial ecosystem service that ensures the reproduction of many plant species, including those that provide food for humans. Climate change is impacting pollination services by altering the phenology (timing) of plant flowering and insect activity. This mismatch between pollinators and their food sources can lead to reduced pollination rates, impacting crop yields and food security.
Water Purification
Ecosystems, particularly wetlands and forests, play a vital role in purifying water by filtering out pollutants and sediment. Climate change is affecting water quality through increased runoff, altered hydrological cycles, and the spread of invasive species. These changes can lead to contaminated water sources, posing risks to human health and aquatic ecosystems.
Carbon Sequestration
Forests and other ecosystems act as natural carbon sinks, absorbing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Climate change is impacting carbon sequestration by increasing the frequency and intensity of wildfires, droughts, and pest outbreaks. These events can lead to the release of stored carbon back into the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change and further impacting ecosystem services.
Economic and Social Costs of Biodiversity Loss
The loss of biodiversity due to climate change has significant economic and social consequences. The decline in ecosystem services, such as pollination and water purification, can lead to reduced crop yields, increased healthcare costs, and diminished tourism revenue. For example, the decline in honeybee populations due to climate change has led to significant losses in agricultural productivity, impacting food security and livelihoods.Furthermore, climate change-induced biodiversity loss can exacerbate social inequalities, disproportionately affecting vulnerable communities that rely heavily on ecosystem services.
For instance, coastal communities facing sea-level rise and increased storm surges are particularly vulnerable to the loss of coastal ecosystems that provide protection from flooding and erosion.The economic and social costs of biodiversity loss due to climate change are far-reaching and underscore the urgent need for effective conservation and adaptation measures to mitigate the impacts of climate change and preserve the essential services provided by ecosystems.
Research and Monitoring

To effectively address the impacts of climate change on biodiversity, comprehensive research and monitoring are crucial. Understanding the complex interactions between climate change and biodiversity requires a multidisciplinary approach, integrating various scientific disciplines. Furthermore, continuous monitoring programs are essential for tracking changes in biodiversity over time and informing conservation strategies.
Key Research Areas
- Predicting Species Distribution Shifts:Climate change is altering habitat suitability for many species, leading to range shifts and potential extinctions. Research focuses on developing models to predict species distribution changes under different climate scenarios, helping to identify areas of high conservation priority.
- Assessing Climate Change Impacts on Ecosystem Services:Ecosystems provide essential services like pollination, water filtration, and carbon sequestration. Research aims to quantify the impacts of climate change on these services, highlighting the economic and social consequences of biodiversity loss.
- Investigating Climate Change-Induced Evolutionary Adaptations:Some species may be able to adapt to climate change through evolutionary processes. Research explores the genetic basis of adaptation, identifying populations that are resilient to climate change and potential mechanisms for enhancing adaptation.
- Understanding the Role of Climate Change in Invasive Species Spread:Climate change can create opportunities for invasive species to establish and spread, threatening native biodiversity. Research focuses on identifying the pathways of invasion, predicting future spread, and developing strategies for managing invasive species.
Importance of Long-Term Monitoring Programs
Long-term monitoring programs are essential for tracking changes in biodiversity over time and informing conservation efforts. They provide valuable data on species abundance, distribution, and population trends, allowing researchers to identify early warning signs of climate change impacts and assess the effectiveness of conservation interventions.
- Identifying Trends and Patterns:Long-term monitoring data can reveal long-term trends in biodiversity, highlighting species that are particularly vulnerable to climate change and identifying potential tipping points in ecosystem function.
- Evaluating Conservation Strategies:Monitoring data can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of conservation interventions, such as habitat restoration or species reintroduction programs, in mitigating climate change impacts on biodiversity.
- Informing Policy Decisions:Long-term monitoring data provide evidence-based information for policymakers to develop effective conservation strategies and allocate resources to address climate change threats to biodiversity.
Role of Citizen Science, Climate change affects biodiversity
Citizen science plays a vital role in collecting data on climate change impacts on biodiversity. By engaging volunteers in data collection, citizen science programs can expand the spatial and temporal scope of monitoring efforts, increasing the amount of data available for research and conservation.
- Increasing Data Collection Capacity:Citizen science programs can significantly increase the amount of data collected, covering areas that may be difficult or expensive to monitor using traditional methods.
- Raising Awareness:Participation in citizen science projects can raise public awareness about climate change impacts on biodiversity, fostering a sense of stewardship and promoting conservation action.
- Building Capacity:Citizen science programs can help build capacity for biodiversity monitoring, training volunteers in data collection and identification skills.






