Lionfish, Chickens, and Moldy Grain: A Global Food Crisis
Fresh take hunting invasive lionfish in dominica a 4 5 billion chicken industry consolidation and the moldy grain coming out of ukraines black sea ports – From the invasive lionfish wreaking havoc on Dominica’s marine ecosystem to the consolidation of the global chicken industry and the challenges of exporting moldy grain from Ukraine’s Black Sea ports, our food system is facing a complex web of interconnected challenges.
These seemingly disparate issues are tied together by a common thread: the vulnerability of our global food supply chain and the urgent need for sustainable solutions.
This article delves into these three critical issues, exploring their individual impacts and highlighting how they are interconnected. We’ll examine the ecological, economic, and ethical implications of each challenge, seeking to understand the root causes and potential solutions.
The Lionfish Invasion

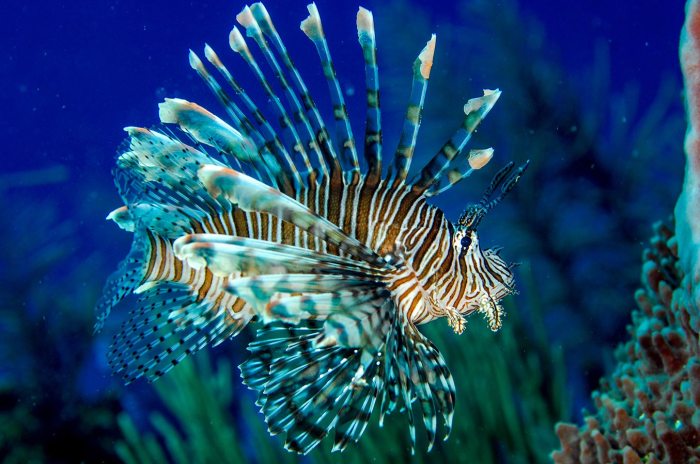
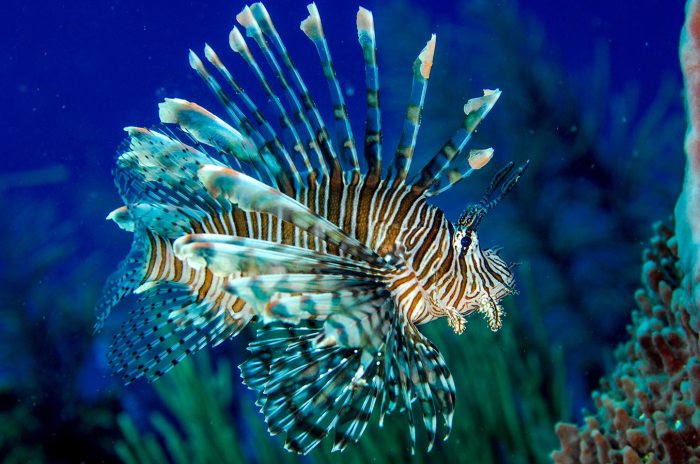
The Caribbean island of Dominica, known for its stunning underwater beauty, is facing a growing threat from an unexpected source: the invasive lionfish. These venomous fish, with their distinctive spiky fins, have rapidly spread throughout the region, wreaking havoc on the delicate balance of the marine ecosystem.
It’s fascinating to see how seemingly disparate issues, like the hunt for invasive lionfish in Dominica, the consolidation of the $4.5 billion chicken industry, and the flow of moldy grain from Ukraine’s Black Sea ports, all intersect. To understand the complexities of these global challenges, we need to delve deeper into the interconnectedness of these systems.
For example, transcript deval patrick on the potential impact of climate change on food security and the need for innovative solutions. Ultimately, the way we address these challenges will shape the future of our food systems and the planet itself.
Ecological Impact of Lionfish
Lionfish, native to the Indo-Pacific region, have no natural predators in the Caribbean. This allows them to thrive and outcompete native fish species for food and habitat. Their voracious appetites, coupled with their rapid reproduction rates, have decimated populations of commercially important fish like snapper, grouper, and lobster.
This decline in native fish populations not only affects the livelihoods of local fishermen but also disrupts the entire food web, leading to cascading effects throughout the ecosystem.
It’s crazy to think about how these seemingly disparate events – like hunting invasive lionfish in Dominica, the consolidation of a $4.5 billion chicken industry, and the influx of moldy grain from Ukraine’s Black Sea ports – can all be connected.
It’s a reminder that the world is interconnected, and even seemingly small events can have ripple effects. And while we’re on the topic of unexpected changes, the news that Iran’s morality police will not bother women, as announced by the president is definitely a significant development.
It’s hard to predict how these events will unfold, but one thing is for sure: we’re living in a time of rapid change, and it’s exciting to see how these shifts will shape the world around us.
Challenges of Controlling the Lionfish Population
Eradicating lionfish from the Caribbean is a daunting task. Their ability to reproduce quickly and their venomous spines make traditional fishing methods ineffective. Moreover, the vastness of the Caribbean Sea makes it difficult to monitor and control their spread.
Innovative Methods for Hunting and Removing Lionfish
To combat the lionfish invasion, scientists and conservationists are exploring innovative approaches. One promising method involves the use of specialized traps designed to capture lionfish while minimizing bycatch. Another approach involves training local fishermen to become lionfish hunters, utilizing spearfishing techniques and encouraging the consumption of lionfish as a food source.
It’s fascinating how seemingly disparate topics like hunting invasive lionfish in Dominica, the consolidation of a $4-5 billion chicken industry, and the flow of moldy grain from Ukraine’s Black Sea ports can be connected. The world is a complex web of interconnected issues, and it’s important to consider how these seemingly isolated events might impact each other.
For instance, the need to develop resilient food systems in the face of global disruptions is driving investment in technologies like AI, as seen in Amazon’s recent £8 billion investment in UK cloud and AI infrastructure. This investment could have far-reaching implications for how we approach challenges like food security and resource management, potentially influencing how we tackle issues like the invasive lionfish problem in Dominica.
Sustainable Fishing Practices in Dominica
Dominica has a long history of sustainable fishing practices, which are crucial for managing the impact of the lionfish invasion. Traditional fishing methods, such as using handlines and hook-and-line techniques, minimize bycatch and promote responsible fishing. Additionally, Dominica has implemented regulations to protect certain fish species during their breeding season and to establish marine reserves where fishing is prohibited, allowing fish populations to recover.
The Global Chicken Industry
The global chicken industry has undergone significant transformation in recent decades, characterized by a dramatic consolidation of production and processing. This trend has resulted in a handful of multinational corporations controlling a large portion of the global chicken market, with far-reaching implications for consumers, farmers, and the environment.
Consolidation and its Impact
The consolidation of the global chicken industry has led to the emergence of a few dominant players, with significant consequences for the industry’s structure, competitiveness, and overall performance.
- Increased Market Concentration:Consolidation has resulted in a decrease in the number of independent chicken producers, leading to increased market concentration. This can reduce competition and potentially limit choices for consumers.
- Control over Supply Chains:Large corporations often control various stages of the chicken supply chain, from breeding and hatching to processing and distribution. This vertical integration can provide efficiency benefits but also raises concerns about market power and potential exploitation of smaller players.
- Price Volatility:The dominance of a few large players can create price volatility in the chicken market, making it difficult for consumers and smaller producers to predict and manage costs.
Ethical Implications of Factory Farming
Factory farming practices, often employed by large-scale chicken producers, have raised significant ethical concerns.
- Animal Welfare:The intensive confinement of chickens in factory farms raises concerns about animal welfare, with potential for overcrowding, disease outbreaks, and inadequate access to space and natural behaviors.
- Antibiotic Use:The use of antibiotics in factory farming has contributed to the rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, posing a public health threat.
- Labor Conditions:Concerns have been raised about working conditions in factory farms, including potential for low wages, unsafe working environments, and limited worker rights.
Environmental Footprint of Large-Scale Chicken Production
Large-scale chicken production has a significant environmental footprint, contributing to a range of environmental issues.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions:Chicken production generates greenhouse gas emissions, primarily from manure management and feed production. These emissions contribute to climate change.
- Water Use:Chicken production requires significant amounts of water for drinking, cleaning, and feed production, putting pressure on water resources.
- Land Use:The expansion of large-scale chicken production can lead to deforestation and habitat loss, impacting biodiversity.
Challenges Faced by Small-Scale Chicken Farmers
Small-scale chicken farmers face a number of challenges in a consolidated industry.
- Competition:Small-scale farmers often struggle to compete with the economies of scale enjoyed by large corporations, leading to difficulties in securing fair prices for their products.
- Access to Markets:Small-scale farmers may face challenges in accessing markets and finding buyers for their produce, particularly in the face of large-scale retailers’ preference for dealing with major suppliers.
- Lack of Resources:Small-scale farmers may lack access to financial resources, technical support, and other resources that can help them compete effectively.
Ukraine’s Black Sea Ports

The conflict in Ukraine has had a devastating impact on global food security, particularly affecting grain exports from the country’s Black Sea ports. The disruption of these vital shipping routes has led to a surge in global food prices and heightened concerns about food shortages, especially in developing countries heavily reliant on Ukrainian wheat and other grains.
Adding to the challenges is the issue of mold contamination in the grain stored in Ukraine, further complicating the already precarious situation.
Factors Contributing to Mold Contamination
Mold contamination in Ukrainian grain is a serious concern, primarily due to the prolonged storage conditions and the lack of proper drying facilities. The following factors contribute to the problem:
- Damage to Infrastructure:The war has damaged grain storage facilities and transportation infrastructure, hindering the efficient movement and processing of grain.
- Power Outages:Frequent power outages caused by the conflict disrupt drying operations, leading to increased moisture content in the grain, which creates a favorable environment for mold growth.
- Limited Access to Drying Facilities:The limited availability of drying facilities, especially in war-affected areas, further exacerbates the problem, as grain cannot be dried quickly enough to prevent mold growth.
- Lack of Adequate Storage Conditions:The storage conditions for grain in Ukraine are often subpar, lacking proper ventilation and temperature control, further contributing to mold development.
Impact of Moldy Grain on Food Security and Safety
Mold contamination in grain poses significant risks to food security and safety. Moldy grain can:
- Reduce Nutritional Value:Mold growth degrades the nutritional value of grain, reducing its protein content and essential vitamins.
- Produce Mycotoxins:Some molds produce mycotoxins, which are toxic substances that can cause various health problems, including liver damage, immune suppression, and cancer.
- Impact Food Safety:Moldy grain can contaminate other food products, leading to food spoilage and posing health risks to consumers.
Challenges of Exporting Grain from Ukraine’s Black Sea Ports
Exporting grain from Ukraine’s Black Sea ports presents several challenges, including:
- Mine Threat:The presence of mines in the Black Sea poses a significant threat to shipping, hindering the safe passage of vessels carrying grain.
- Limited Shipping Capacity:The reduced number of available ships and the limited capacity of Ukrainian ports further restrict the volume of grain that can be exported.
- Insurance Costs:The high insurance costs associated with shipping grain through the Black Sea due to the risks involved make it financially challenging for exporters.
- Inspection Delays:The need for rigorous inspections of grain for mold contamination and other quality issues can lead to delays in export processes.
Strategy for Mitigating the Risks Associated with Moldy Grain
To mitigate the risks associated with moldy grain, a comprehensive strategy is needed, encompassing the following key elements:
- Improving Grain Storage Infrastructure:Investing in modern grain storage facilities with proper ventilation, temperature control, and drying capabilities is crucial for preventing mold growth.
- Ensuring Access to Drying Facilities:Expanding access to drying facilities, especially in war-affected areas, is essential for reducing moisture content in grain and minimizing mold contamination.
- Implementing Strict Quality Control Measures:Implementing rigorous quality control measures throughout the grain supply chain, from harvesting to export, is essential for identifying and removing contaminated grain.
- Developing Effective Mold Control Strategies:Investing in research and development to develop effective mold control strategies, including the use of biocontrol agents and innovative drying techniques, is critical for minimizing mold contamination.
The Interconnectedness of Global Challenges: Fresh Take Hunting Invasive Lionfish In Dominica A 4 5 Billion Chicken Industry Consolidation And The Moldy Grain Coming Out Of Ukraines Black Sea Ports
Our world faces a multitude of interconnected challenges, each impacting the others in complex and often unexpected ways. The lionfish invasion, the consolidation of the global chicken industry, and the Ukrainian grain crisis are three seemingly disparate issues, but they share a common thread: they all impact our global food system and highlight the need for a more sustainable and interconnected approach to problem-solving.
Comparing and Contrasting Global Challenges, Fresh take hunting invasive lionfish in dominica a 4 5 billion chicken industry consolidation and the moldy grain coming out of ukraines black sea ports
The lionfish invasion, a biological threat originating in the Indo-Pacific, has disrupted the delicate balance of the Caribbean ecosystem. The global chicken industry, dominated by a few multinational corporations, faces challenges related to animal welfare, environmental sustainability, and food security.
The Ukrainian grain crisis, a result of the ongoing war, has disrupted global grain supply chains and driven up food prices, particularly in developing countries. While these challenges differ in their origins and immediate impacts, they share common themes:
- Impact on Food Security:The lionfish invasion disrupts local fisheries, impacting livelihoods and food availability. The chicken industry’s focus on efficiency can lead to food insecurity if disruptions occur in its supply chain. The Ukrainian grain crisis directly impacts food security, particularly in regions reliant on Ukrainian exports.
- Environmental Sustainability:The lionfish invasion is a consequence of human-induced environmental changes. The chicken industry faces criticism for its environmental impact, including greenhouse gas emissions and water pollution. The Ukrainian grain crisis has highlighted the vulnerability of global food systems to geopolitical instability and the need for more resilient agricultural practices.
- Economic Impacts:The lionfish invasion negatively affects the tourism industry and fishing communities. The chicken industry’s consolidation has led to reduced competition and potential price manipulation. The Ukrainian grain crisis has caused food price inflation and economic hardship in many countries.
Potential for Collaboration and Solutions
Recognizing the interconnectedness of these challenges presents an opportunity for collaborative solutions. For example:
- Sustainable Fishing Practices:Promoting sustainable fishing methods to control the lionfish population can benefit the local fishing industry while also protecting the ecosystem.
- Diversification of Food Production:Encouraging diversification in food production, reducing reliance on a few dominant players, can create a more resilient food system and address concerns about the consolidation of the chicken industry.
- Strengthening Global Food Supply Chains:Investing in resilient food supply chains, including alternative sources of grain and transportation routes, can mitigate the impacts of crises like the Ukrainian grain crisis.
Interconnections within the Global Food System
These challenges are deeply interconnected within the global food system:
- Global Trade and Interdependence:The lionfish invasion highlights the interconnectedness of ecosystems, while the Ukrainian grain crisis showcases the vulnerability of global trade routes.
- Climate Change and Food Security:Climate change exacerbates the impacts of the lionfish invasion and can disrupt the chicken industry’s production. The Ukrainian grain crisis also highlights the need to address climate change and its impact on food production.
- Consumption Patterns and Food Waste:Changing consumer preferences and reducing food waste are essential for addressing the challenges of the chicken industry and ensuring sustainable food systems.
Importance of Sustainable Practices
Addressing these global challenges requires a shift towards sustainable practices in all aspects of the food system.
“Sustainability is not just about the environment, it’s about the economy and society as well. It’s about creating a world that works for everyone, now and in the future.”
- Responsible Aquaculture:Promoting responsible aquaculture practices can help address the lionfish invasion and provide a sustainable source of protein.
- Ethical and Sustainable Farming:Promoting ethical and sustainable farming practices within the chicken industry can improve animal welfare and reduce environmental impact.
- Investment in Agricultural Resilience:Investing in agricultural research and development can help create more resilient food systems, better prepared to face future challenges.