Will Housing Prices Flatten or Collapse?
Analysis will housing prices flatten or collapse – Will Housing Prices Flatten or Collapse? This question is on the minds of many as we navigate a complex and rapidly evolving housing market. It’s a question that demands careful analysis, considering a multitude of factors that are shaping the future of homeownership.
From interest rate fluctuations to economic uncertainty, from supply chain disruptions to global events, the housing market is facing a perfect storm of challenges.
This blog delves into the intricacies of the housing market, exploring the key drivers that are influencing price trends. We’ll examine the current market conditions, analyze economic factors, and explore the dynamics of supply and demand. We’ll also discuss the role of government policies, investor sentiment, and technological advancements in shaping the future of housing prices.
Current Housing Market Trends: Analysis Will Housing Prices Flatten Or Collapse

The housing market is a complex and dynamic system influenced by a multitude of factors, including economic conditions, interest rates, demographics, and government policies. Understanding current trends and their underlying drivers is crucial for navigating the market, whether you are a buyer, seller, or investor.
Recent trends in housing prices have varied significantly across different regions. While some areas have experienced rapid appreciation, others have seen slower growth or even declines. This variation is partly attributed to the unique characteristics of each local market, such as employment opportunities, affordability, and supply and demand dynamics.
The question of whether housing prices will flatten or collapse is a complex one, influenced by a multitude of factors. While the recent news of junior doctors accepting a 22% pay rise to end strikes might seem unrelated, it highlights the broader economic pressures that could impact the housing market.
Ultimately, the future of housing prices depends on a delicate balance of economic indicators, and it’s impossible to predict with certainty whether we’ll see a dramatic shift or a gradual stabilization.
Factors Influencing Current Market Conditions
The current housing market is influenced by a confluence of factors, including:
- Interest Rates:Rising interest rates have made mortgages more expensive, cooling demand and putting downward pressure on prices in some areas. However, the impact of interest rates varies depending on the specific market and the sensitivity of buyers to changes in borrowing costs.
- Inflation:High inflation has eroded purchasing power and contributed to increased housing costs, making affordability a growing concern for many potential buyers.
- Supply and Demand:The balance between supply and demand is a key driver of housing prices. In areas with limited housing inventory and strong demand, prices tend to rise. Conversely, areas with abundant supply and weak demand may experience price declines or stagnation.
- Economic Conditions:The overall health of the economy influences housing market activity. Strong economic growth, low unemployment, and rising wages typically support housing demand. Conversely, economic downturns or recessions can lead to reduced demand and price corrections.
- Government Policies:Government policies, such as tax incentives, regulations, and zoning laws, can impact the housing market. For example, policies aimed at increasing housing affordability or stimulating construction can influence supply and demand dynamics.
Comparison to Previous Housing Cycles, Analysis will housing prices flatten or collapse
The current housing market bears some similarities to previous cycles, but also has unique characteristics. For example, the rapid appreciation seen in recent years echoes the boom of the early 2000s, but the current market is also characterized by high inflation, rising interest rates, and supply chain disruptions, which were not as prominent in the previous cycle.
The question of whether housing prices will flatten or collapse is a complex one, with many factors at play. The recent rise in interest rates has certainly put pressure on the market, but it’s important to consider the broader economic picture.
It’s encouraging to see that Asia Pacific markets opened higher today, tracking rises in the Dow and S&P 500 , suggesting a degree of confidence in the global economy. This positive sentiment could potentially influence the housing market as well, although it’s too early to say for sure.
Understanding the historical context of housing cycles is crucial for assessing current market conditions and making informed decisions. Historical data can provide insights into the duration of booms and busts, the impact of various factors on prices, and the potential for future market adjustments.
Economic Factors Influencing Housing Prices
Economic factors play a crucial role in determining the trajectory of housing prices. Understanding these factors is essential for anyone trying to predict whether housing prices will flatten or collapse. Factors like interest rates, inflation, consumer confidence, and economic recession all exert significant influence on the housing market.
Impact of Interest Rates on Housing Affordability
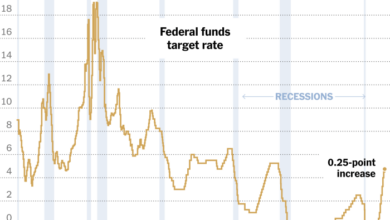
Interest rates are a primary driver of housing affordability. When interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing money for a mortgage increases, making it more expensive for buyers to purchase homes. This can lead to a decrease in demand for housing, which can put downward pressure on prices.
Conversely, when interest rates fall, borrowing becomes cheaper, increasing demand and potentially driving prices up. For example, in 2022, the Federal Reserve aggressively raised interest rates to combat inflation. This resulted in a significant increase in mortgage rates, which quickly cooled the housing market.
Many potential buyers found themselves priced out of the market, leading to a slowdown in home sales and a decrease in price growth.
“Higher interest rates make it more expensive to borrow money, which can lead to a decrease in demand for housing and put downward pressure on prices.”
Role of Inflation and Consumer Confidence in Housing Demand
Inflation, which is a general increase in prices for goods and services, can also affect housing demand. When inflation is high, consumers may have less disposable income to spend on housing, leading to a decrease in demand. Additionally, high inflation can erode consumer confidence, making people hesitant to make large purchases like a home.
On the other hand, low inflation and strong consumer confidence can boost housing demand. When consumers feel optimistic about the economy and their own financial situation, they are more likely to purchase homes. This can lead to increased demand and potentially higher prices.
“High inflation can erode consumer confidence, making people hesitant to make large purchases like a home.”
Potential Effects of Economic Recession on the Housing Market
An economic recession can have a significant impact on the housing market. During a recession, unemployment rates tend to rise, leading to a decrease in consumer spending and a decline in housing demand. This can lead to a drop in home prices and a slowdown in sales.
For example, during the Great Recession of 2008-2009, the housing market experienced a severe downturn. Unemployment soared, consumer confidence plummeted, and many homeowners found themselves underwater on their mortgages. This led to a wave of foreclosures and a significant decline in home prices.
Predicting whether housing prices will flatten or collapse is a complex issue, especially when considering global economic factors. One interesting angle to consider is what’s stalling China’s stock market recovery, as outlined in this article whats stalling chinas stock market recovery according to kraneshares cio.
The article highlights key challenges like investor confidence and regulatory uncertainty, which could have ripple effects on global markets and ultimately influence housing trends.
“During a recession, unemployment rates tend to rise, leading to a decrease in consumer spending and a decline in housing demand.”
Supply and Demand Dynamics

The interaction of supply and demand plays a crucial role in determining housing prices. Understanding the current state of housing supply and demand is essential to predict whether prices will flatten or collapse.
Current Housing Supply
The current housing supply is characterized by a persistent shortage, which has been a contributing factor to the recent surge in prices. This shortage is attributed to several factors, including:
- Limited New Construction:The pace of new home construction has lagged behind demand, primarily due to factors such as rising construction costs, labor shortages, and regulatory hurdles. This has resulted in a limited supply of new homes entering the market, further exacerbating the existing shortage.
- Aging Housing Stock:The existing housing stock is aging, with a significant portion of homes requiring repairs or renovations. This has reduced the number of available units, further contributing to the supply shortage.
- Shifting Housing Preferences:Changing preferences among homebuyers, such as a desire for more space or specific amenities, have led to a mismatch between the available housing stock and current demand.
Factors Influencing New Construction
The rate of new construction is a key factor influencing housing supply. Several factors impact the pace of new home construction:
- Construction Costs:Rising costs of materials, labor, and land have made it more expensive to build new homes, deterring some developers from starting new projects.
- Interest Rates:Higher interest rates make mortgages more expensive, reducing affordability for potential homebuyers and potentially slowing down demand for new homes.
- Land Availability:The availability of suitable land for development is a significant constraint, particularly in urban areas where land is scarce and expensive.
- Regulatory Environment:Complex permitting processes, zoning regulations, and environmental regulations can create significant hurdles for developers, slowing down the construction process.
Impact of Demographic Trends on Housing Demand
Demographic trends have a significant impact on housing demand. Factors such as population growth, household formation, and aging populations influence the number of homes needed.
- Population Growth:As the population grows, the demand for housing increases. This is particularly true in areas experiencing rapid population growth, where the demand for housing can outpace supply.
- Household Formation:Changes in household formation, such as rising divorce rates and an increase in single-person households, can impact housing demand. For example, an increase in single-person households could lead to higher demand for smaller, more affordable housing units.
- Aging Population:As the population ages, demand for housing shifts towards more age-appropriate homes, such as single-story homes with accessible features. This can create a shortage of suitable housing for older adults, particularly in areas with limited housing options.
Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations play a significant role in shaping the housing market, influencing affordability, accessibility, and overall market stability. Recent changes in housing policies, along with government incentives and regulatory adjustments, have had a tangible impact on housing prices, creating both opportunities and challenges for buyers and sellers.
Impact of Recent Housing Policies on the Market
Recent housing policies have aimed to address affordability concerns and stimulate homeownership. For example, the expansion of tax credits for first-time homebuyers has made homeownership more accessible for certain segments of the population. Conversely, stricter lending regulations have made it more difficult for some borrowers to qualify for mortgages, potentially slowing down market activity.
These policies have created a complex interplay of forces that affect housing prices, with varying outcomes depending on the specific market conditions.
Government Incentives for Homeownership
Government incentives, such as tax credits and subsidies, can play a vital role in boosting homeownership rates. These incentives can lower the cost of homeownership, making it more attainable for individuals and families who might otherwise struggle to enter the market.
However, the effectiveness of such incentives depends on factors like eligibility criteria, program design, and market demand.
Potential Effects of Regulatory Changes on Housing Prices
Regulatory changes can significantly impact housing prices by affecting supply, demand, and financing options. For instance, zoning regulations that limit new construction can contribute to housing shortages, driving up prices. Similarly, changes in mortgage lending standards can affect the availability of financing, influencing affordability and market activity.
For example, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, enacted in 2010, introduced stricter lending regulations, which led to a decrease in mortgage originations and a slowdown in home sales.
Global Economic Influences
The global economy exerts a significant influence on housing markets worldwide. Fluctuations in global economic conditions, international investment trends, and geopolitical events can all impact housing prices and market dynamics.
International Investment in Housing Markets
International investment plays a crucial role in shaping housing markets, particularly in major cities and desirable locations. Foreign investors often seek to diversify their portfolios and capitalize on potential appreciation in housing values. This influx of capital can contribute to rising prices, especially in areas where demand outpaces supply.
- Increased Demand:International investors often drive up demand for housing, particularly in sought-after locations. This increased demand can lead to price appreciation and a more competitive market.
- Foreign Currency Fluctuations:Changes in exchange rates can impact the affordability of housing for international buyers. A stronger domestic currency makes housing more expensive for foreign investors, potentially dampening demand.
- Investment Strategies:International investors may employ various strategies, such as purchasing properties for rental income or holding them for long-term appreciation. These strategies can influence housing market trends and pricing dynamics.
Geopolitical Events and Housing Prices
Geopolitical events, such as wars, political instability, or natural disasters, can have significant implications for housing markets. These events can disrupt economic activity, impact investor confidence, and lead to shifts in housing demand and supply.
- Economic Uncertainty:Geopolitical events often create economic uncertainty, which can make investors hesitant to invest in housing markets. This can lead to a decline in demand and potentially lower prices.
- Refugee Flows:In the event of conflicts or disasters, refugee flows can create a surge in demand for housing in specific locations. This can lead to temporary price increases in affected areas.
- Government Policies:Governments may implement policies to address the impacts of geopolitical events on housing markets, such as providing financial assistance to displaced individuals or offering tax incentives to stimulate investment.