Bill Gates Says This Is The Worlds Deadliest Animal, And The Data Shows Hes Right
Bill gates says this is the worlds deadliest animal and the data shows hes right – Bill Gates Says This Is The World’s Deadliest Animal, And The Data Shows He’s Right. It’s not a lion, a shark, or even a venomous snake. The culprit? The humble mosquito. These tiny insects, often seen as a nuisance, are responsible for the deaths of millions of people each year, more than any other animal on the planet.
While we might swat at them with annoyance, the reality is that mosquitoes are silent killers, spreading deadly diseases across the globe.
The impact of mosquito-borne diseases extends far beyond the immediate loss of life. These illnesses place a significant burden on healthcare systems, cripple economies, and hinder development, particularly in low-income countries. The World Health Organization estimates that malaria alone, a mosquito-borne disease, is responsible for nearly half a million deaths annually, primarily among children under five.
Understanding the threat posed by mosquitoes is crucial to developing effective strategies for control and prevention, ultimately saving lives and improving the well-being of communities worldwide.
The Deadliest Animal
Bill Gates, the co-founder of Microsoft and philanthropist, famously declared that the deadliest animal in the world is not a lion, shark, or any other large predator, but rather a tiny insect: the mosquito. This statement might seem surprising, but the data clearly supports his claim.
While other animals pose threats to humans, mosquitoes are responsible for transmitting deadly diseases that claim millions of lives each year.
Impact of Mosquitoes on Human Health
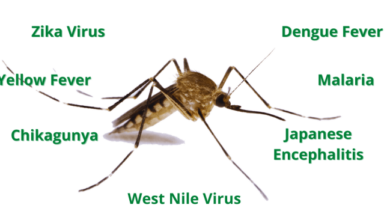
Mosquitoes are vectors for a variety of diseases that can have devastating consequences for human health. The most significant mosquito-borne diseases include malaria, dengue fever, yellow fever, Zika virus, and West Nile virus. These diseases can cause a range of symptoms, from mild fevers and rashes to severe organ damage, neurological complications, and even death.
Mosquito-Borne Diseases: A Leading Cause of Death
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that there are approximately 241 million cases of malaria each year, resulting in an estimated 627,000 deaths. Dengue fever, another mosquito-borne disease, affects an estimated 390 million people annually, with around 20,000 deaths. These figures highlight the significant impact of mosquito-borne diseases on global health.
Mortality Rates Compared to Other Causes of Death
When comparing the mortality rates of mosquito-borne diseases to other major causes of death globally, it becomes clear that these diseases are a significant public health concern. For example, the number of deaths attributed to malaria each year is higher than the number of deaths caused by HIV/AIDS.
While other factors like heart disease and stroke contribute to a larger number of deaths globally, mosquito-borne diseases disproportionately impact developing countries, where access to healthcare and resources is often limited.
Mosquito-Borne Diseases
Mosquitoes are more than just a nuisance; they are a significant threat to global health, responsible for spreading a range of debilitating and often deadly diseases. These diseases affect millions of people worldwide, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions.
Malaria
Malaria is a life-threatening disease caused by a parasite that is transmitted through the bite of infected mosquitoes. It is prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, where it accounts for a significant portion of child mortality.
Malaria symptoms typically appear 10 to 15 days after the mosquito bite and include fever, chills, sweating, headache, muscle pain, and fatigue. If left untreated, malaria can be fatal. Treatment involves antimalarial drugs, which are effective in killing the parasite and preventing complications.
Prevention strategies include:
- Using insecticide-treated mosquito nets
- Applying insect repellent
- Wearing long-sleeved clothing and pants
- Eliminating mosquito breeding grounds by draining standing water
Dengue Fever, Bill gates says this is the worlds deadliest animal and the data shows hes right
Dengue fever is a viral infection spread through the bite of infected Aedes mosquitoes. It is prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions of the world, including Southeast Asia, Latin America, and the Caribbean. Symptoms of dengue fever typically appear 4 to 10 days after the mosquito bite and include high fever, severe headache, muscle and joint pain, and rash.
In some cases, dengue fever can progress to a more severe form, known as dengue hemorrhagic fever, which can lead to internal bleeding and organ failure.Treatment for dengue fever focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. There is no specific antiviral treatment available.
Prevention strategies include:
- Using insect repellent
- Wearing long-sleeved clothing and pants
- Eliminating mosquito breeding grounds by draining standing water
Zika Virus
Zika virus is a mosquito-borne illness spread through the bite of infected Aedes mosquitoes. It is prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions, including the Americas, Africa, and Asia.Symptoms of Zika virus infection are often mild and include fever, rash, joint pain, and conjunctivitis (red eyes).
Bill Gates’ assertion that mosquitos are the world’s deadliest animal might seem surprising, but the data backs it up. While we might think of lions or sharks as the most dangerous creatures, it’s the tiny mosquito that spreads deadly diseases like malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus.
It’s a stark reminder of how interconnected our world is, and how even the smallest of creatures can have a profound impact on our lives. In a separate but related issue, anti-abortion doctors are urging the Supreme Court to keep mifepristone restrictions in place , a decision that could have a significant impact on women’s healthcare access.
It’s a complex issue with far-reaching implications, and it’s crucial to stay informed and engaged in the ongoing dialogue.
However, Zika virus infection during pregnancy can lead to serious birth defects, including microcephaly, a condition in which the baby’s head is smaller than normal. Treatment for Zika virus infection focuses on managing symptoms. There is no specific antiviral treatment available.
Prevention strategies include:
- Using insect repellent
- Wearing long-sleeved clothing and pants
- Eliminating mosquito breeding grounds by draining standing water
West Nile Virus
West Nile virus is a mosquito-borne illness spread through the bite of infected Culex mosquitoes. It is prevalent in North America, Europe, Africa, and the Middle East.Most people infected with West Nile virus experience no symptoms or only mild symptoms, such as fever, headache, body aches, and fatigue.
However, in some cases, the infection can lead to serious complications, including encephalitis (inflammation of the brain) and meningitis (inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord).Treatment for West Nile virus infection focuses on managing symptoms. There is no specific antiviral treatment available.
Prevention strategies include:
- Using insect repellent
- Wearing long-sleeved clothing and pants
- Eliminating mosquito breeding grounds by draining standing water
The Impact of Mosquitoes on Development

Mosquitoes are more than just a nuisance; they are a significant threat to global development. The diseases they transmit, such as malaria, dengue fever, Zika virus, and yellow fever, pose a major burden on individuals, communities, and nations. These diseases can hinder development efforts, particularly in low-income countries, by draining resources, impacting productivity, and hindering access to education and healthcare.
Bill Gates’ claim that mosquitoes are the world’s deadliest animal might seem surprising, but the data backs it up. It’s a sobering reminder of the power of tiny creatures to impact our lives. And speaking of unexpected impacts, it’ll be interesting to see if will Breton’s final salvo rock Von der Leyen’s boat even further in the ongoing political drama.
Just like mosquitoes, even small actions can have huge consequences, whether we’re talking about public health or international politics.
Economic Burden of Mosquito-Borne Diseases
The economic burden of mosquito-borne diseases is substantial. These diseases result in significant healthcare costs, lost productivity, and reduced economic growth. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that malaria alone costs Africa an estimated $12 billion annually in lost productivity and healthcare expenses.
The impact of these diseases extends beyond individual households, affecting entire communities and nations.
- Healthcare Costs:The treatment and prevention of mosquito-borne diseases consume a significant portion of healthcare budgets, especially in low-income countries. This often leaves limited resources for other essential health services.
- Lost Productivity:Mosquito-borne illnesses can lead to absenteeism from work and school, reducing productivity and economic output. This impact is particularly pronounced in agricultural communities, where individuals rely on physical labor for their livelihoods.
- Reduced Economic Growth:The economic burden of these diseases can hinder overall economic growth. The decline in productivity, healthcare costs, and tourism revenue can significantly impact national development.
Impact on Development Efforts
Mosquito-borne diseases can hinder development efforts in various ways, particularly in low-income countries. These diseases can exacerbate poverty, limit access to education and healthcare, and impede progress towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Poverty:The economic burden of these diseases can trap individuals and communities in poverty. The costs of treatment, lost wages, and reduced productivity can significantly strain household budgets, making it difficult to escape poverty.
- Education:Mosquito-borne illnesses can disrupt school attendance, particularly among children. The illnesses can lead to absenteeism, school dropouts, and reduced learning outcomes, ultimately hindering human capital development.
- Healthcare:The high prevalence of mosquito-borne diseases can strain healthcare systems, diverting resources from other essential services. This can lead to limited access to quality healthcare for other conditions, exacerbating health inequalities.
Impact on Education, Healthcare, and Productivity
Mosquito-borne diseases have a direct impact on education, healthcare, and productivity. These diseases can lead to absenteeism, reduced learning outcomes, and diminished workforce participation.
- Education:Mosquito-borne diseases, particularly malaria, can significantly impact school attendance and learning outcomes. The illnesses can lead to absenteeism, reduced cognitive function, and increased risk of school dropout.
- Healthcare:The high prevalence of these diseases places a significant burden on healthcare systems, diverting resources and personnel from other essential services. This can lead to limited access to quality healthcare for other conditions, exacerbating health inequalities.
- Productivity:Mosquito-borne illnesses can lead to reduced productivity in the workforce. The illnesses can cause absenteeism, reduced work capacity, and increased healthcare costs, impacting economic growth and development.
Strategies for Mosquito Control
Mosquito control is crucial to reducing the burden of mosquito-borne diseases and protecting human health. A multifaceted approach is necessary to effectively manage mosquito populations, considering various factors like the species involved, the environment, and the potential impact on the ecosystem.
Insecticide Spraying
Insecticide spraying is a widely used method for controlling mosquito populations. This approach involves applying insecticides to areas where mosquitoes breed or rest, aiming to kill adult mosquitoes or prevent larvae from developing.
Bill Gates famously pointed out that mosquitos are the world’s deadliest animal, and the statistics back him up. But while those tiny insects spread diseases that claim millions of lives each year, we shouldn’t forget about the devastating impacts of climate change.
The recent deadly Pakistan floods are a climate catastrophe, says UN chief , a stark reminder that the planet’s health is intertwined with our own. The floods are a tragedy, and they highlight the urgency of addressing climate change, which will only exacerbate these kinds of extreme weather events.
- Ultra-Low Volume (ULV) Spraying:ULV spraying uses a fine mist of insecticide that can cover a large area, effectively targeting adult mosquitoes in flight. It is often used for emergency response to outbreaks of mosquito-borne diseases or for large-scale mosquito control programs.
- Space Spraying:This method involves spraying insecticide into the air to kill adult mosquitoes. Space spraying is commonly used for public health purposes, such as controlling mosquito populations in urban areas or during special events.
- Residual Spraying:Residual spraying involves applying insecticides to surfaces, such as walls and ceilings, where mosquitoes rest. The insecticide remains active for a period of time, killing mosquitoes that come into contact with the treated surfaces.
While insecticide spraying can be effective in reducing mosquito populations, it also has drawbacks.
- Environmental Impact:Insecticides can harm non-target organisms, including beneficial insects, birds, and aquatic life. The use of certain insecticides can also contribute to the development of insecticide resistance in mosquito populations.
- Human Health Concerns:Some insecticides can be harmful to human health, particularly for people with pre-existing conditions or those who are exposed to high concentrations.
It is essential to use insecticides judiciously, following safety guidelines and minimizing potential risks to human health and the environment.
Habitat Modification
Modifying mosquito breeding habitats is a crucial aspect of mosquito control. This approach focuses on eliminating or reducing mosquito breeding sites, disrupting the mosquito life cycle and reducing their populations.
- Drainage:Removing standing water from areas where mosquitoes breed is a fundamental approach. This can involve draining stagnant water from containers, ditches, and other areas.
- Filling:Filling in low-lying areas that collect water can eliminate mosquito breeding sites. This can be achieved using soil, gravel, or other materials.
- Maintenance:Maintaining drainage systems, such as ditches and gutters, can prevent water from accumulating and creating breeding grounds for mosquitoes.
Habitat modification is a long-term, sustainable approach to mosquito control, minimizing the need for chemical interventions.
Biological Control
Biological control methods utilize natural predators, parasites, or pathogens to control mosquito populations. This approach offers a more environmentally friendly alternative to insecticide spraying.
- Predatory Fish:Introducing fish species that feed on mosquito larvae, such as Gambusia affinis, can help control mosquito populations in ponds, ditches, and other water bodies.
- Mosquito-Eating Birds:Encouraging the presence of birds that feed on mosquitoes, such as swallows, can help reduce mosquito populations in areas where these birds are abundant.
- Mosquito-Specific Bacteria:Certain bacteria, such as Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis (Bti), are toxic to mosquito larvae but are not harmful to other organisms. Bti can be applied to water bodies to control mosquito populations.
Biological control methods can be effective in reducing mosquito populations, but they require careful planning and implementation to ensure they are effective and do not have unintended consequences.
Integrated Mosquito Management (IMM)
An integrated approach to mosquito control is essential for long-term success. IMM involves combining various methods, including insecticide spraying, habitat modification, biological control, and public education, to manage mosquito populations effectively.
- Community Involvement:Engaging communities in mosquito control efforts is crucial. This can involve educating residents about mosquito-borne diseases, promoting mosquito prevention measures, and encouraging them to report mosquito breeding sites.
- Surveillance and Monitoring:Regular surveillance and monitoring of mosquito populations are essential to identify areas where mosquito populations are high and to track the effectiveness of control measures.
- Targeted Interventions:Implementing control measures that are targeted to specific mosquito species and breeding habitats can be more effective and minimize environmental impact.
IMM is a comprehensive and sustainable approach to mosquito control, promoting a balance between human health, environmental protection, and community involvement.
The Role of Technology in Mosquito Control: Bill Gates Says This Is The Worlds Deadliest Animal And The Data Shows Hes Right
The battle against mosquitoes has become increasingly sophisticated, with technology playing a crucial role in enhancing our efforts to control these disease-carrying insects. From advanced traps to drone-based spraying, innovative solutions are being developed to combat the threat posed by mosquitoes.
Mosquito Traps
Mosquito traps are a fundamental component of mosquito control, using various methods to lure and capture mosquitoes.
- Light traps:These traps attract mosquitoes using ultraviolet light, mimicking the natural light sources that attract them.
- Carbon dioxide traps:These traps emit carbon dioxide, mimicking the human breath, which attracts mosquitoes.
- Ovi-traps:These traps target mosquito eggs by providing a suitable breeding ground for them, allowing for the control of mosquito populations before they mature.
Advanced traps can also incorporate features like automated data collection and remote monitoring, enabling researchers to track mosquito populations and understand their behavior.
Drones for Insecticide Spraying
Drones have emerged as a highly effective tool for insecticide spraying, offering several advantages over traditional methods.
- Precision targeting:Drones can be programmed to spray insecticides precisely in targeted areas, minimizing the impact on surrounding environments and non-target species.
- Increased efficiency:Drones can cover vast areas quickly and efficiently, enabling large-scale mosquito control operations.
- Accessibility:Drones can access difficult-to-reach areas, such as dense vegetation or swampy terrains, where traditional methods are ineffective.
However, the use of drones in insecticide spraying raises concerns about potential environmental and health risks. Careful planning and monitoring are crucial to ensure the safe and responsible use of drones in mosquito control.
Genetic Modification
Genetic modification is a relatively new approach to mosquito control, involving altering the genetic makeup of mosquitoes to reduce their population or ability to transmit diseases.
- Gene drives:This technology aims to spread specific genes within a mosquito population, leading to population reduction or the inability to transmit diseases.
- Sterile insect technique (SIT):This technique involves releasing large numbers of genetically modified male mosquitoes that are sterile, reducing the reproductive capacity of the wild population.
While genetic modification offers promising potential for mosquito control, it raises ethical concerns about unintended consequences and the potential impact on ecosystems. Rigorous research and public engagement are essential before widespread implementation.
Technological Solutions for Mosquito Control
| Solution | Functionality | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Mosquito Traps | Attract and capture mosquitoes using various methods like light, carbon dioxide, or ovi-traps. | Reduce mosquito populations in targeted areas, enabling monitoring and research. |
| Drones for Insecticide Spraying | Utilize drones to precisely spray insecticides in targeted areas, minimizing environmental impact. | Efficiently control mosquito populations in large areas, particularly those difficult to access. |
| Genetic Modification | Alter the genetic makeup of mosquitoes to reduce their population or ability to transmit diseases. | Potentially reduce mosquito populations and disease transmission, but raises ethical concerns. |
The Importance of Public Awareness
Public awareness plays a crucial role in preventing mosquito-borne diseases. When people understand the risks associated with mosquito bites and the importance of taking preventive measures, they are more likely to engage in behaviors that reduce their exposure to these insects.
Effective Public Health Campaigns
Public health campaigns can effectively promote mosquito control measures by raising awareness about the risks, providing practical advice, and encouraging community participation. Effective campaigns often employ a combination of strategies, including:
- Informative materials:Brochures, flyers, and posters can disseminate essential information about mosquito-borne diseases, prevention methods, and the importance of mosquito control.
- Public service announcements:Radio and television commercials can reach a wide audience and convey important messages about mosquito control in a concise and memorable way.
- Social media campaigns:Utilizing social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram allows for targeted messaging and interactive engagement, fostering community participation and sharing of information.
- Community outreach programs:Engaging with local communities through workshops, presentations, and door-to-door campaigns can provide tailored information and answer questions specific to the area.
Recommendations for Individual Protection
Individuals can take several steps to protect themselves from mosquito bites. Here are some recommendations:
- Use insect repellent:Apply insect repellent containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus according to product instructions.
- Wear protective clothing:When outdoors, wear long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and light-colored clothing to minimize exposed skin.
- Avoid peak mosquito hours:Mosquitoes are most active during dawn and dusk, so try to limit outdoor activities during these times.
- Eliminate mosquito breeding grounds:Remove standing water from containers, such as flower pots, birdbaths, and tires, to prevent mosquito larvae from developing.
- Use mosquito nets:When sleeping outdoors or in areas with high mosquito populations, use mosquito nets to protect yourself from bites.