Is There a National Teacher Shortage? Heres What We Know and Dont Know
Is there a national teacher shortage heres what we know and dont know – Is There a National Teacher Shortage? Here’s What We Know and Don’t Know sets the stage for a deep dive into the current state of education in America. We’ll explore the facts, the challenges, and the potential solutions to this pressing issue.
The shortage isn’t just a matter of numbers; it’s a reflection of the complex pressures facing educators today, from low pay and lack of support to increasing workloads and changing societal expectations. This exploration aims to shed light on the realities of the teacher shortage and its impact on students, schools, and the future of education.
This topic is multifaceted, and it’s important to approach it with a nuanced perspective. While there’s no denying the existence of a shortage, understanding the contributing factors, the consequences, and the potential solutions requires careful consideration. We’ll delve into the research, examine the statistics, and consider the voices of educators themselves to paint a comprehensive picture of this complex issue.
Defining the Teacher Shortage: Is There A National Teacher Shortage Heres What We Know And Dont Know
The United States is currently facing a significant teacher shortage, with educators leaving the profession at alarming rates and a dwindling pool of qualified candidates to fill vacant positions. This shortage has far-reaching consequences for students, impacting their access to quality education and ultimately hindering their future success.
Current State of the Teacher Shortage
The teacher shortage is a complex issue with multifaceted causes, and its severity varies across regions and subject areas. Statistics reveal a stark reality:
- Vacancies: According to the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), the number of teacher vacancies in public schools has been steadily increasing in recent years. In 2021, there were an estimated 800,000 teacher vacancies nationwide, a significant jump from previous years.
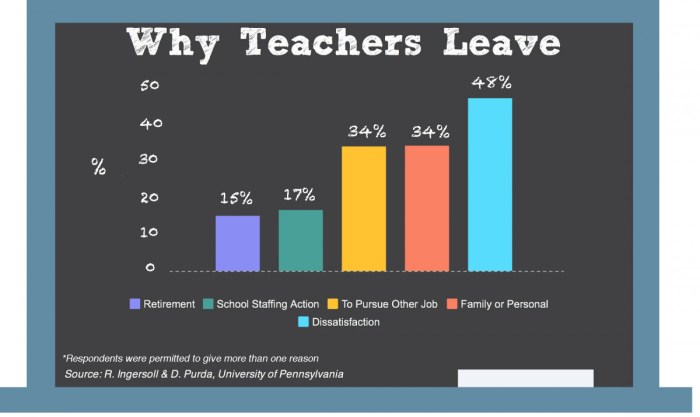
- Turnover Rates: The National Education Association (NEA) reports that teacher turnover rates have also been on the rise. In 2022, the average teacher turnover rate was 14%, meaning that nearly one in seven teachers left their positions each year. This high turnover rate is a major contributor to the teacher shortage, as it creates a constant need for new teachers to fill vacated roles.
Regions and Subject Areas Most Affected
The teacher shortage is not uniformly distributed across the country. Certain regions and subject areas are particularly hard-hit, facing a more acute crisis than others:
- Rural Areas: Rural schools often struggle to attract and retain teachers due to limited resources, lower salaries, and a lack of amenities. This makes it difficult to compete with schools in more urban areas, which can offer higher salaries and better working conditions.
The national teacher shortage is a complex issue, with many factors contributing to the problem. One factor that’s often overlooked is the lack of investment in STEM education, which could be hindering the development of future educators. Just like the UK’s inability to retain its top tech firms, as highlighted in this recent article former arm ceo criticizes britain for not holding onto its top tech firms , a lack of strategic planning can have long-term consequences.
Investing in STEM education, and creating a more supportive environment for teachers, could be a crucial step towards addressing the national teacher shortage.
- Special Education: Special education teachers are in high demand, as students with disabilities require specialized instruction and support. However, the number of qualified special education teachers is often insufficient to meet the growing need, creating a significant shortage in this critical area.
- STEM Subjects: Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) subjects are experiencing a shortage of qualified teachers. This is partly due to the increasing demand for STEM professionals in the workforce, which makes it more attractive for STEM graduates to pursue careers outside of education.
Historical Context of Teacher Shortages, Is there a national teacher shortage heres what we know and dont know
Teacher shortages are not a new phenomenon. Throughout history, there have been periods of teacher shortages, often driven by factors such as economic downturns, wars, or societal shifts. However, the current teacher shortage is considered to be particularly severe, driven by a combination of factors that have converged in recent years.
- Declining Public Support for Education: In recent decades, there has been a decline in public support for education, leading to lower funding levels and increased pressure on schools to do more with less. This has made the teaching profession less attractive to potential candidates, who may perceive it as underpaid and undervalued.
- Increased Bureaucracy and Accountability: The education system has become increasingly bureaucratic and accountable, with teachers facing more paperwork, standardized testing, and performance evaluations. This has added to the workload and stress levels of teachers, leading some to leave the profession.
- Changes in the Labor Market: The labor market has become more competitive, with many young people pursuing careers in other fields that offer higher salaries and greater job security. This has made it more difficult to attract qualified individuals to the teaching profession.
Contributing Factors to the Shortage
The teacher shortage is a complex issue with multiple contributing factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing effective solutions to address the problem. While some factors are more prevalent in certain regions or demographics, they all contribute to the overall decline in the teacher workforce.
Low Pay and Compensation
Low pay and lack of competitive compensation packages are significant contributors to the teacher shortage. Teachers are often underpaid compared to other professionals with similar education levels and responsibilities. This disparity in pay can make teaching a less attractive career option, particularly for individuals with high levels of debt from their education.
- A study by the Economic Policy Institute found that teachers’ salaries have stagnated over the past two decades, while the cost of living has continued to rise. This means that teachers are effectively losing purchasing power over time.
- The lack of competitive salaries can also lead to experienced teachers leaving the profession for more lucrative opportunities in other fields.
- The shortage is particularly acute in rural areas and high-poverty schools, where salaries are often lower and working conditions are more challenging.
Lack of Support and Professional Development
Teachers often feel unsupported and undervalued, which can lead to burnout and dissatisfaction with their jobs. This lack of support can manifest in various ways, including inadequate resources, excessive workloads, and limited opportunities for professional development.
- Teachers are often expected to work long hours, including evenings and weekends, to prepare lessons, grade assignments, and attend meetings. This can lead to stress and burnout, particularly for teachers with families or other commitments.
- Many teachers feel overwhelmed by the increasing demands placed on them, including the need to meet new standards and assessments, address student mental health needs, and implement new technologies in the classroom.
- Limited opportunities for professional development can also contribute to teacher dissatisfaction. Teachers need ongoing support and training to stay up-to-date on best practices and effectively address the diverse needs of their students.
Increasing Workload and Stress
The workload of teachers has been steadily increasing in recent years, leading to increased stress and burnout. This is due to a combination of factors, including larger class sizes, increased accountability measures, and the need to address the growing mental health needs of students.
- Teachers are often expected to teach more students with fewer resources, which can lead to increased stress and decreased job satisfaction.
- The pressure to meet standardized test scores and other accountability measures can also contribute to teacher stress and burnout. This can lead to teachers feeling like they are being evaluated based on factors that are outside of their control.
- Teachers are increasingly being asked to address the mental health needs of their students, which can be a challenging and time-consuming task. This can lead to teachers feeling overwhelmed and unsupported, particularly if they do not have the necessary training and resources.
Negative Public Perception
Teachers are often undervalued and underappreciated by the public. This can lead to a negative perception of the teaching profession, which can discourage young people from pursuing careers in education.
- Teachers are often portrayed in a negative light in the media, which can contribute to a negative public perception of the profession.
- The public may not fully understand the challenges and complexities of teaching, which can lead to unrealistic expectations and a lack of appreciation for the work that teachers do.
- This negative perception can discourage talented individuals from entering the teaching profession, further exacerbating the teacher shortage.
Table of Contributing Factors
| Factor | Impact | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Low Pay and Compensation | Teachers are underpaid, leading to a lack of attraction to the profession and experienced teachers leaving for better-paying jobs. | Increase teacher salaries, offer competitive benefits packages, and provide incentives for working in high-need areas. |
| Lack of Support and Professional Development | Teachers feel unsupported and undervalued, leading to burnout and dissatisfaction. | Provide adequate resources, reduce workload, and offer more opportunities for professional development. |
| Increasing Workload and Stress | Teachers are overwhelmed by increasing demands, leading to stress and burnout. | Reduce class sizes, provide more support staff, and address the mental health needs of students. |
| Negative Public Perception | The teaching profession is undervalued and underappreciated, discouraging talented individuals from entering the field. | Promote positive narratives about teaching, increase public awareness of the challenges and complexities of the profession, and celebrate the achievements of teachers. |
The Impact of the Shortage on Education
The teacher shortage is not just a matter of statistics; it has real, tangible consequences for students, schools, and the future of education. The lack of qualified educators can significantly impact student learning, access to quality education, and the overall educational landscape.
Consequences for Student Learning
The impact of the teacher shortage on student learning is multifaceted and can manifest in various ways. One of the most significant concerns is the potential for students to be taught by unqualified or underprepared teachers. This can lead to a decline in the quality of instruction, limiting students’ opportunities to learn and achieve their full potential.
- Access to Qualified Teachers:In areas with a severe shortage, schools may struggle to fill positions, leading to a higher reliance on unqualified teachers or those with limited experience. This can compromise the quality of education students receive, potentially hindering their academic progress and future prospects.
The national teacher shortage is a complex issue with no easy solutions. While we know there’s a growing demand for educators and a shrinking pool of qualified candidates, pinpointing the exact causes is challenging. It’s easy to get distracted by sensational headlines like trump blames harris biden for second assassination attempt their rhetoric is causing me to be shot at , but we need to focus on the real issues affecting our classrooms.
Ultimately, finding solutions to the teacher shortage requires a multifaceted approach, addressing factors like low pay, increased workload, and a lack of support for educators.
- Increased Class Sizes:Teacher shortages can lead to larger class sizes, making it more challenging for teachers to provide individual attention and support to each student. This can negatively impact student engagement, learning outcomes, and overall academic achievement.
- Limited Course Offerings:Schools may have to cut back on elective courses or specialized programs due to a lack of qualified teachers. This can restrict students’ opportunities to explore their interests, develop new skills, and prepare for future careers.
Hypothetical Scenario
Imagine a rural school district facing a severe teacher shortage. With limited resources and a dwindling pool of qualified candidates, the district is forced to hire teachers who may not have the necessary expertise or experience. This can lead to a situation where students are taught by teachers who are not adequately prepared to handle the curriculum or meet the diverse learning needs of their students.
Additionally, the lack of qualified teachers can result in larger class sizes, making it difficult for teachers to provide individual attention and support to each student. This can lead to a decline in student achievement and a widening of the achievement gap between students from different socioeconomic backgrounds.
The teacher shortage is a complex issue, with factors ranging from low pay to burnout playing a role. It’s interesting to think about how this relates to Dua Lipa’s recent comments about some artists being ruthless in sharing their private lives, which she discussed in a recent interview.
While the worlds of education and celebrity might seem different, both professions involve personal sacrifices and public scrutiny. Perhaps we can learn from the way some artists navigate their personal lives in the public eye and apply it to supporting teachers better.
Initiatives to Mitigate the Impact
While the teacher shortage poses significant challenges, various initiatives and programs are being implemented to address the issue and mitigate its impact on education. These initiatives aim to attract and retain qualified teachers, support their professional development, and create a more supportive and rewarding teaching environment.
- Teacher Loan Forgiveness Programs:These programs offer financial incentives to encourage individuals to pursue teaching careers, particularly in high-need areas. By reducing student loan debt, these programs can make teaching a more financially attractive option.
- Mentorship and Support Programs:Mentorship programs can provide new teachers with guidance, support, and professional development opportunities, helping them succeed in their roles and build confidence. These programs can also create a sense of community and belonging for teachers, making them more likely to stay in the profession.
- Increased Teacher Salaries:Competitive salaries can attract and retain qualified teachers, particularly in areas where the cost of living is high. By increasing salaries, districts can make teaching a more financially rewarding profession, attracting and retaining talented educators.
Addressing the Shortage
The teacher shortage is a complex issue with no easy solutions. Addressing it requires a multi-pronged approach that tackles the root causes and provides incentives to attract and retain qualified educators.
Strategies for Addressing the Teacher Shortage
Several strategies can be implemented to address the teacher shortage. These strategies aim to increase the attractiveness of the teaching profession, improve working conditions, and provide support to educators.
Increasing Teacher Pay
- Competitive Salaries:One of the most effective ways to attract and retain teachers is to offer competitive salaries. Research consistently shows a strong correlation between teacher pay and teacher quality, student achievement, and teacher retention. For instance, a study by the Economic Policy Institute found that states with higher teacher salaries tend to have higher student achievement scores.
- Salary Increases:Implementing regular salary increases for teachers helps keep their salaries competitive with other professions. This can help prevent experienced teachers from leaving the profession for higher-paying jobs.
- Performance-Based Pay:Performance-based pay systems, such as merit pay or bonuses, can be used to reward teachers who demonstrate exceptional performance. However, these systems should be carefully designed to avoid unintended consequences, such as encouraging teachers to focus on teaching to the test.
Providing More Support
- Mentorship Programs:Mentorship programs can provide new teachers with guidance and support from experienced educators. This can help new teachers navigate the challenges of the profession and build confidence.
- Professional Development Opportunities:Providing teachers with access to professional development opportunities can help them stay up-to-date on the latest research and best practices. This can help them improve their teaching skills and stay motivated.
- Reduced Class Sizes:Smaller class sizes can reduce the workload for teachers and allow them to provide more individualized attention to students. This can lead to improved student outcomes and a more supportive teaching environment.
Improving Working Conditions
- Reduced Administrative Burden:Teachers often spend a significant amount of time on administrative tasks that take away from their time with students. Reducing the administrative burden can make the teaching profession more appealing and allow teachers to focus on their primary responsibility: teaching.
- Increased Autonomy:Giving teachers more autonomy in their classrooms can make them feel more valued and respected. This can lead to increased job satisfaction and retention.
- Positive School Climate:Creating a positive school climate where teachers feel supported and valued can have a significant impact on teacher morale and retention. This can involve providing teachers with a voice in school decisions and fostering a culture of collaboration.
Effectiveness of Strategies
- Salary Increases:Research has shown that salary increases can lead to improved teacher quality, student achievement, and teacher retention. However, the effectiveness of salary increases may vary depending on the specific context and the amount of the increase.
- Mentorship Programs:Mentorship programs have been shown to be effective in helping new teachers transition into the profession and improve their teaching skills.
- Professional Development Opportunities:High-quality professional development opportunities can help teachers improve their teaching skills and stay up-to-date on the latest research and best practices.
Policy Recommendations
- Increase Funding for Education:Increased funding for education can be used to increase teacher salaries, provide more support for teachers, and reduce class sizes.
- Expand Teacher Training Programs:Expanding teacher training programs can help address the shortage of qualified teachers. This can involve increasing the number of teacher education programs and providing financial incentives for students to enter the teaching profession.
- Promote Teacher Retention:Implementing policies that promote teacher retention, such as providing support for new teachers, reducing administrative burdens, and creating a positive school climate, can help address the teacher shortage.
The Future of the Teacher Shortage

Predicting the future of the teacher shortage is a complex task, involving numerous interconnected factors. The demographic landscape, technological advancements, and evolving societal values all play a role in shaping the future of teaching. Understanding these trends can provide valuable insights into potential scenarios for the teacher shortage in the years to come.
Demographic Shifts and Their Impact
Demographic shifts, particularly an aging population and declining birth rates, can significantly influence the future of the teacher shortage. As the population ages, there will be a greater demand for educators to cater to the needs of an increasingly diverse student body.
Simultaneously, declining birth rates could lead to a smaller pool of potential teachers in the future. These demographic trends could exacerbate the existing teacher shortage, making it more challenging to fill open positions.
Technological Advancements and Their Influence
Technological advancements are transforming the education landscape, offering both opportunities and challenges for the future of teaching. Emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and virtual reality (VR), could potentially disrupt traditional teaching methods and create new roles for educators.
For example, AI-powered tutoring systems could provide personalized learning experiences, while VR simulations could offer immersive and engaging learning environments. While these advancements have the potential to enhance teaching and learning, they also raise concerns about the potential displacement of teachers.
Evolving Societal Values and Their Implications
Societal values are constantly evolving, and this evolution can influence the attractiveness of the teaching profession. Factors such as work-life balance, job security, and compensation can impact the decision of individuals to enter or remain in the teaching profession.
For instance, if societal values shift towards prioritizing work-life balance, teaching may become more attractive to individuals seeking flexible work arrangements. Conversely, if societal values prioritize high salaries and career advancement, the teaching profession may become less appealing to individuals seeking lucrative career paths.
Potential Scenarios for the Future of the Teacher Shortage
Based on the factors discussed above, it is possible to envision several potential scenarios for the future of the teacher shortage:
- Optimistic Scenario:In an optimistic scenario, proactive measures to address the teacher shortage, such as increased teacher salaries, improved working conditions, and greater investment in teacher training and development, could lead to a more attractive teaching profession. This, combined with technological advancements that enhance teaching and learning, could create a more sustainable and fulfilling career path for educators.
As a result, the teacher shortage could gradually ease, with a sufficient number of qualified teachers to meet the needs of the student population.
- Pessimistic Scenario:In a pessimistic scenario, the teacher shortage could continue to worsen, fueled by demographic shifts, declining teacher morale, and insufficient investment in education. This could lead to larger class sizes, fewer specialized courses, and a decline in the quality of education.
The shortage could also create a vicious cycle, as fewer qualified teachers lead to a less attractive teaching profession, further discouraging individuals from entering the field.
- Hybrid Scenario:A hybrid scenario is also possible, where the teacher shortage is partially mitigated by technological advancements and innovative approaches to teaching. For example, the use of online learning platforms and blended learning models could help to alleviate the pressure on teachers, allowing them to focus on personalized instruction and student support.
However, this scenario could also lead to a widening gap between students who have access to technology and those who do not, exacerbating existing inequalities in education.