Mosquito-Borne Diseases: What You Need to Know
What to know about the elevated risks of mosquito borne diseases – Mosquito-Borne Diseases: What You Need to Know sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Mosquitoes, those tiny, buzzing insects, are more than just a nuisance; they are silent carriers of deadly diseases that affect millions worldwide.
From malaria to dengue fever, these illnesses can cause severe health complications, disrupt communities, and strain economies. This exploration dives into the world of mosquito-borne diseases, examining the factors that contribute to their spread, the devastating consequences they bring, and the strategies we can employ to combat them.
Understanding the intricate relationship between mosquitoes, diseases, and human health is crucial for protecting ourselves and our communities. We will delve into the science behind mosquito-borne diseases, explore the environmental and social factors that contribute to their spread, and discuss the multifaceted approach needed to mitigate their impact.
Whether you’re a concerned citizen, a traveler planning a trip to an endemic area, or simply someone curious about these silent threats, this information is essential for making informed decisions and taking proactive steps to safeguard your well-being.
Understanding Mosquito-Borne Diseases
Mosquito-borne diseases are a significant global health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide. These diseases are spread through the bite of infected mosquitoes, which act as vectors, transmitting pathogens from one person to another. Understanding these diseases is crucial for preventing their spread and protecting individuals and communities.
Types of Mosquito-Borne Diseases
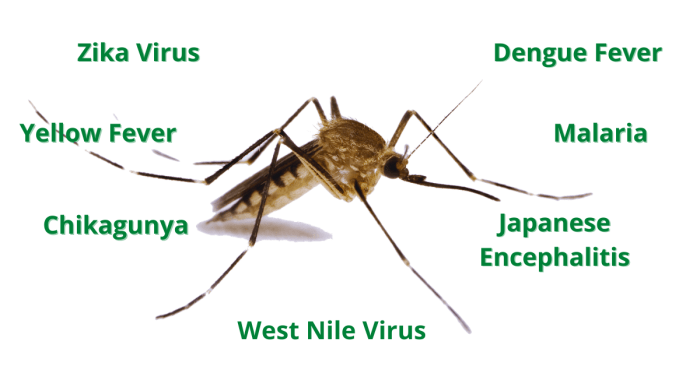
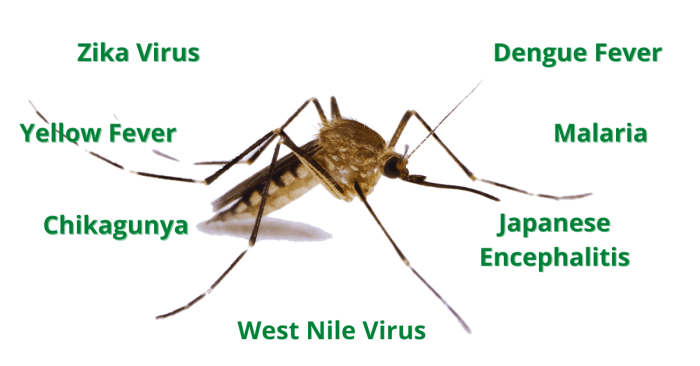
Mosquito-borne diseases encompass a wide range of illnesses caused by various pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, and parasites. Some of the most common and concerning mosquito-borne diseases include:
- Malaria: Caused by a parasite called -Plasmodium*, transmitted by the bite of an infected -Anopheles* mosquito. Symptoms include fever, chills, sweating, headache, and muscle aches. Malaria is prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions, particularly in Africa, Asia, and South America.
- Dengue Fever: Caused by the dengue virus, transmitted by the bite of an infected -Aedes* mosquito. Symptoms include high fever, severe headache, muscle and joint pain, and rash. Dengue fever is found in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide, including Southeast Asia, Latin America, and the Caribbean.
- Zika Virus: Caused by the Zika virus, transmitted by the bite of an infected -Aedes* mosquito. Symptoms include fever, rash, joint pain, and conjunctivitis (red eyes). Zika virus infection during pregnancy can lead to birth defects in infants. Zika virus is prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas, Africa, Asia, and the Pacific Islands.
- Chikungunya: Caused by the chikungunya virus, transmitted by the bite of an infected -Aedes* mosquito. Symptoms include high fever, severe joint pain, headache, and muscle pain. Chikungunya is found in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide, including Africa, Asia, and the Americas.
- Yellow Fever: Caused by the yellow fever virus, transmitted by the bite of an infected -Aedes* mosquito. Symptoms include fever, headache, muscle aches, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes). Yellow fever is prevalent in tropical regions of South America and Africa.
- West Nile Virus: Caused by the West Nile virus, transmitted by the bite of an infected -Culex* mosquito. Most people infected with West Nile virus experience no symptoms, but some develop mild flu-like symptoms, while others experience more severe neurological complications. West Nile virus is found in North America, Europe, Africa, and the Middle East.
Mosquito Vectors
Mosquitoes play a crucial role in the transmission of these diseases. Different species of mosquitoes are responsible for transmitting different diseases. For example:
- *Anopheles* mosquitoes are the primary vectors for malaria, while -Aedes* mosquitoes transmit dengue fever, Zika virus, and chikungunya.
- *Culex* mosquitoes are responsible for transmitting West Nile virus.
Mosquito Life Cycle and Disease Transmission
Mosquitoes undergo a complete metamorphosis, with four distinct stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult.
- Eggs: Mosquitoes lay their eggs in water, typically in stagnant water sources like ponds, puddles, and containers.
- Larvae: The eggs hatch into larvae, which live in water and feed on algae and organic matter.
- Pupae: Larvae develop into pupae, which are inactive and remain in the water.
- Adults: Adult mosquitoes emerge from the pupae and are capable of flying and feeding on blood.
Female mosquitoes need blood to produce eggs. When a female mosquito bites an infected person, it ingests the pathogen. The pathogen then multiplies in the mosquito’s body and can be transmitted to other people when the mosquito bites them. The time it takes for the pathogen to develop in the mosquito, known as the extrinsic incubation period, varies depending on the disease and the environmental conditions.
Mosquito-borne diseases are a growing concern, especially with changing climates and increased urbanization. It’s important to be aware of the risks and take precautions, like using insect repellent and wearing protective clothing. While we’re on the topic of protection, I just saw zendaya just made culottes look chill while coordinating white tank tops with tom holland – talk about a stylish way to stay covered! Anyway, back to mosquitoes – it’s also crucial to eliminate standing water in your yard, as this is where mosquitoes breed.
By taking these steps, we can help protect ourselves and our families from these dangerous diseases.
Factors Contributing to Elevated Risks
The incidence of mosquito-borne diseases is on the rise globally, and several factors contribute to this concerning trend. Understanding these factors is crucial for implementing effective prevention and control strategies.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a significant role in shaping the spread of mosquito-borne diseases.
- Climate Change:Rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns create favorable conditions for mosquito breeding and survival. Warmer temperatures accelerate mosquito development, leading to shorter life cycles and increased breeding potential.
- Urbanization:Rapid urbanization often results in the creation of suitable breeding grounds for mosquitoes, such as stagnant water in gutters, drainage ditches, and unmaintained swimming pools.
- Stagnant Water Sources:The presence of stagnant water provides ideal breeding grounds for mosquitoes. This can be due to inadequate drainage systems, overflowing sewage, or neglected water bodies.
Human Behavior
Human behavior significantly impacts the risk of mosquito-borne diseases.
- Travel to Endemic Areas:Increased global travel exposes individuals to mosquito-borne diseases in endemic regions. This can lead to the introduction of new pathogens into previously unaffected areas.
- Lack of Mosquito Control Measures:Inadequate mosquito control measures, such as the use of mosquito nets, repellents, and insecticides, can contribute to the spread of diseases.
- Inadequate Sanitation:Poor sanitation practices, such as improper waste disposal and open defecation, create favorable conditions for mosquito breeding and disease transmission.
Vulnerability of Different Populations
Different populations exhibit varying levels of vulnerability to mosquito-borne diseases.
Mosquito-borne diseases are a growing concern, especially as climate change alters mosquito habitats. It’s important to be aware of the risks, especially if you’re traveling to areas with a high prevalence of these diseases. Even places you might consider “boring” can harbor these insects.
Take, for instance, the UK town so dull it was ranked the fifth most boring place on earth , which still has its fair share of mosquitos. So, no matter where you’re going, remember to protect yourself with mosquito repellent and take precautions to prevent bites.
- Age:Infants and young children are particularly vulnerable due to their developing immune systems.
- Health Status:Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, are at higher risk of severe complications from mosquito-borne diseases.
- Socioeconomic Conditions:Poverty and lack of access to healthcare services can exacerbate the vulnerability of populations to mosquito-borne diseases.
Health Impacts and Consequences: What To Know About The Elevated Risks Of Mosquito Borne Diseases
The consequences of mosquito-borne diseases extend far beyond a simple itchy bite. These diseases can lead to a range of health complications, from mild discomfort to severe illness, disability, and even death. The impact of these diseases is not limited to individuals; they can also have devastating effects on communities and economies.
Impact of Mosquito-Borne Diseases
Mosquito-borne diseases have a profound impact on individuals, communities, and economies.
Mosquito-borne diseases are on the rise, and it’s important to be aware of the risks, especially during warmer months. From Zika to West Nile, these diseases can be serious, so taking precautions is crucial. Speaking of serious, did you see the article about Halle Berry finally addressing the jokes about her characters’ wigs in that recent interview?
halle berry has seen the jokes about her characters jacked up wigs exclusive Anyway, back to mosquitos, remember to wear repellent, drain standing water, and stay vigilant to protect yourself and your family.
Impact on Individuals
- Physical Health:Mosquito-borne diseases can cause a wide range of symptoms, including fever, headache, muscle aches, fatigue, rash, and joint pain. Some diseases, like dengue fever and malaria, can lead to severe complications, including organ failure, bleeding, and death.
- Mental Health:The fear of contracting a mosquito-borne disease can lead to anxiety and stress, particularly in areas where these diseases are prevalent. Long-term illness and disability can also have a significant impact on mental well-being.
- Financial Burden:Medical expenses associated with mosquito-borne diseases can be substantial, particularly for those without adequate health insurance. This can lead to financial hardship and even bankruptcy.
Impact on Communities
- Public Health Crisis:Outbreaks of mosquito-borne diseases can overwhelm healthcare systems, leading to shortages of medical supplies and personnel. This can result in delays in diagnosis and treatment, further increasing the risk of severe illness and death.
- Economic Impact:Mosquito-borne diseases can have a significant impact on economies, particularly in developing countries. They can disrupt agricultural production, reduce tourism, and increase healthcare costs.
- Social Disruption:Outbreaks of mosquito-borne diseases can lead to social disruption, as people avoid public gatherings and travel to minimize their risk of exposure. This can disrupt education, work, and social activities.
Impact on Economies
- Healthcare Costs:The treatment of mosquito-borne diseases can be expensive, placing a significant burden on healthcare systems. This can lead to higher healthcare costs for individuals and governments.
- Loss of Productivity:Mosquito-borne diseases can cause illness and disability, leading to lost productivity in the workforce. This can have a negative impact on economic growth.
- Tourism Decline:Outbreaks of mosquito-borne diseases can deter tourists from visiting affected areas, leading to a decline in tourism revenue.
Global Burden of Mosquito-Borne Diseases
The global burden of mosquito-borne diseases is significant. Millions of people are infected with these diseases each year, and hundreds of thousands die.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 700,000 people die from mosquito-borne diseases each year.
The global distribution of mosquito-borne diseases is uneven, with the highest burden in tropical and subtropical regions.
Prevention and Control Strategies
Preventing mosquito-borne diseases requires a multi-pronged approach encompassing personal protective measures, environmental management, and vector control strategies. This section delves into these strategies, aiming to equip individuals with the knowledge and tools to minimize their risk of contracting mosquito-borne illnesses.
Personal Protective Measures
Personal protective measures play a crucial role in preventing mosquito bites and subsequent infections. These measures involve strategies that individuals can implement to reduce their exposure to mosquitoes.
- Use insect repellent:Applying insect repellent containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus can effectively deter mosquitoes. Repellents should be applied according to product instructions and reapplied regularly, especially after sweating or swimming.
- Wear protective clothing:Covering exposed skin with long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and socks can significantly reduce mosquito bites. Light-colored clothing can be more effective than dark colors in reflecting sunlight and making it harder for mosquitoes to spot you.
- Stay indoors during peak mosquito activity:Mosquitoes are most active at dawn and dusk, so it is advisable to limit outdoor activities during these times. If you must be outside, consider using mosquito nets or staying in screened areas.
- Eliminate standing water:Mosquitoes breed in stagnant water, so it is essential to eliminate potential breeding grounds around your home. This includes emptying water-filled containers, such as flower pots, bird baths, and buckets, and ensuring gutters are clean and free of obstructions.
Environmental Management, What to know about the elevated risks of mosquito borne diseases
Environmental management focuses on modifying the environment to reduce mosquito breeding and survival. This involves measures that target mosquito habitats and prevent their proliferation.
- Maintain vegetation:Mosquitoes often breed in overgrown vegetation, so keeping lawns and gardens trimmed and free of excessive foliage can help minimize their breeding sites.
- Drain standing water:Eliminating stagnant water sources, such as puddles, ditches, and clogged drains, is crucial in preventing mosquito breeding. This can be achieved through proper drainage systems and regular maintenance.
- Control water sources:Managing water sources, such as swimming pools, ponds, and irrigation systems, is essential for preventing mosquito breeding. This includes ensuring proper chlorination of pools, maintaining water levels in ponds, and using mosquito control measures in irrigation systems.
Vector Control
Vector control methods directly target mosquito populations to reduce their numbers and minimize disease transmission. These methods involve various strategies, including the use of insecticides, larvicides, and biological control agents.
- Insecticide-Treated Nets (ITNs):ITNs are widely used for malaria prevention, particularly in areas with high transmission rates. These nets are treated with insecticides that kill or repel mosquitoes when they come into contact with the net. ITNs are most effective when used consistently and properly, ensuring full coverage of the bed and avoiding holes or tears.
- Larvicides:Larvicides are insecticides that target mosquito larvae in their breeding grounds. These chemicals are typically applied to water bodies, either in granular form or as a liquid solution. Larvicides can be effective in reducing mosquito populations before they reach adulthood and become capable of transmitting diseases.
- Biological Control:Biological control involves using natural predators or parasites to control mosquito populations. This method is considered more environmentally friendly than using chemical insecticides. Examples include introducing mosquito-eating fish to ponds or releasing larvivorous mosquitoes that prey on other mosquito larvae.
Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment of mosquito-borne diseases are crucial for minimizing complications and improving patient outcomes. Prompt medical attention and appropriate treatment can significantly reduce the severity of illness and prevent long-term health consequences.
- Recognize symptoms:Being aware of the symptoms of common mosquito-borne diseases, such as fever, headache, muscle aches, rash, and joint pain, is essential for seeking medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis allows for timely treatment and can prevent the disease from progressing to a more severe stage.
- Seek medical advice:If you suspect you may have contracted a mosquito-borne disease, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional immediately. They can perform necessary tests to confirm the diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
- Follow treatment plan:Once a diagnosis is confirmed, it is crucial to follow the prescribed treatment plan carefully. This may involve medications, rest, and supportive care. Completing the entire course of treatment is essential for eliminating the infection and preventing complications.
Research and Development
The fight against mosquito-borne diseases is a constant battle, demanding ongoing research and development efforts to find innovative solutions for prevention, treatment, and control. Scientists and researchers worldwide are working tirelessly to develop vaccines, drugs, and other interventions to combat these diseases effectively.
Challenges and Opportunities in Controlling Mosquito Populations
Controlling mosquito populations is crucial to preventing disease transmission. Several challenges hinder effective control, including:
- Resistance to Insecticides:Mosquitoes have developed resistance to many commonly used insecticides, making traditional control methods less effective. This resistance is a significant challenge for public health officials.
- Climate Change:Rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns can expand the geographic range of mosquitoes and increase their breeding potential. Climate change exacerbates the spread of mosquito-borne diseases.
- Urbanization:Rapid urbanization creates ideal breeding grounds for mosquitoes in stagnant water sources like open containers and drainage systems. This poses a significant challenge in densely populated areas.
Despite these challenges, opportunities exist for more effective mosquito control:
- Integrated Vector Management (IVM):This approach combines various control methods, including biological control, insecticide resistance management, and environmental management, to achieve sustainable mosquito control.
- Genetic Modification:Scientists are exploring the use of genetically modified mosquitoes to reduce mosquito populations or prevent disease transmission. This innovative approach holds significant promise for long-term control.
- Novel Insecticides:Research is underway to develop new insecticides that are effective against insecticide-resistant mosquitoes and have minimal environmental impact.
Role of Technology and Innovation in Combating Mosquito-Borne Diseases
Technology and innovation play a vital role in combating mosquito-borne diseases:
- Remote Sensing:Satellite imagery and aerial surveillance can identify mosquito breeding grounds and monitor mosquito populations over large areas.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):AI algorithms can analyze data from various sources, including mosquito traps and weather patterns, to predict disease outbreaks and optimize control efforts.
- Mobile Technology:Mobile apps can educate the public about mosquito-borne diseases, provide information on prevention measures, and report mosquito sightings.