Indias No to 9/11 Legacy: A Nations Response
Indias no to 9 11 legacy – India’s No to 9/11 Legacy: A Nation’s Response explores how the September 11th attacks shaped India’s domestic and foreign policy, impacting its relationship with the United States and its own fight against terrorism. The attacks were a watershed moment, forcing India to confront its own vulnerabilities and to reassess its role in a world suddenly grappling with a new kind of threat.
The aftermath of 9/11 saw India take decisive steps to strengthen its counterterrorism apparatus, enacting new legislation, enhancing intelligence sharing, and collaborating with global partners to dismantle terrorist networks. The attacks also marked a turning point in India-US relations, leading to closer cooperation on security and strategic issues.
India’s Response to 9/11

The 9/11 attacks, a defining moment in global history, profoundly impacted India’s foreign policy and domestic security landscape. India’s response to the attacks was marked by a blend of empathy, strategic considerations, and a renewed focus on combating terrorism.
India’s Immediate Reaction
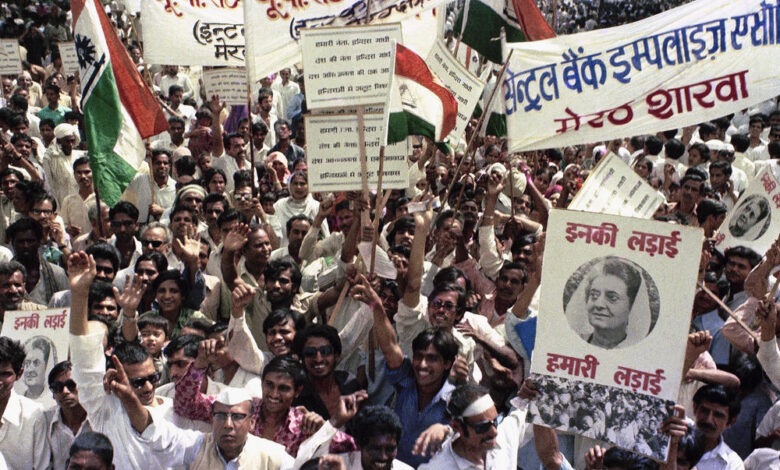
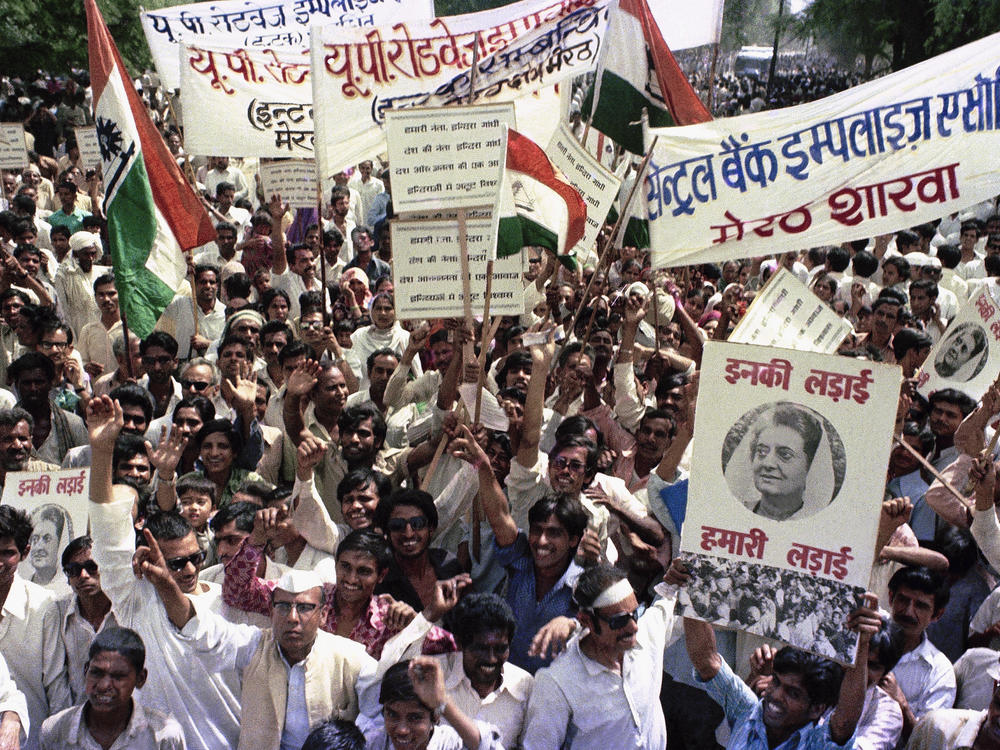
India swiftly condemned the 9/11 attacks, offering condolences to the United States and expressing solidarity with the American people. Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee, in a statement to the nation, declared that “terrorism is a global menace” and that India stood “shoulder to shoulder” with the United States in the fight against it.
Public sentiment in India was one of shock and outrage, with widespread condemnation of the attacks and support for the US in its efforts to combat terrorism.
India’s Strategic Considerations
The 9/11 attacks presented India with a unique opportunity to strengthen its ties with the United States, a key player in global security. India recognized the shared threat posed by terrorism and saw the attacks as an opportunity to forge a strategic partnership with the US.
The aftermath of 9/11 witnessed a significant shift in the US’s approach to South Asia, with a greater focus on combating terrorism and a willingness to engage with India as a key partner. This shift created a favorable environment for India to advance its own interests in the region.
India’s Domestic Security Measures
Following 9/11, India implemented a range of domestic security measures to enhance its counter-terrorism capabilities. These included:
- Anti-Terrorism Legislation:India enacted several anti-terrorism laws, including the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA) and the Prevention of Terrorism Act (POTA), aimed at strengthening law enforcement agencies’ powers to combat terrorism.
- Law Enforcement Strategies:The Indian government strengthened its intelligence gathering and sharing mechanisms, improved coordination between various security agencies, and adopted a more proactive approach to tackling terrorism. This involved increased surveillance, stricter border controls, and enhanced security measures at public places.
- Strengthening Counter-Terrorism Infrastructure:India invested heavily in modernizing its security forces, acquiring advanced technology, and establishing specialized counter-terrorism units. The National Security Guard (NSG), a highly trained counter-terrorism force, was further strengthened and deployed to combat terrorism effectively.
The Impact of 9/11 on India-US Relations: Indias No To 9 11 Legacy
The attacks of September 11, 2001, marked a pivotal moment in global history and had a profound impact on the trajectory of India-US relations. The shared threat of terrorism, a common enemy in the “war on terror”, brought the two nations closer than ever before, transforming their relationship from one of strategic distance to one of strategic partnership.
A New Era of Cooperation
The 9/11 attacks significantly altered the geopolitical landscape, prompting the US to reassess its foreign policy priorities. This shift opened a new window of opportunity for India, as the US sought to broaden its strategic alliances in the face of a global terrorist threat.
The shared threat of terrorism became a catalyst for closer cooperation, leading to a series of significant agreements and turning points in the India-US relationship.
- The US-India Nuclear Deal (2005):This landmark agreement, a major departure from decades of US policy, allowed India to access civilian nuclear technology while adhering to international non-proliferation norms. The deal was a testament to the growing strategic partnership between the two countries and signaled a new era of cooperation in the nuclear field.
- The US-India Strategic Partnership (2005):This framework, formally established in 2005, Artikeld a comprehensive agenda for bilateral cooperation across a wide range of areas, including defense, counterterrorism, trade, and technology. It solidified the foundation for a long-term strategic partnership between the two nations.
- The US-India Defense Framework Agreement (2005):This agreement laid the groundwork for closer military cooperation, including joint exercises, information sharing, and defense technology transfers. It further deepened the strategic partnership between the two countries and facilitated a more robust collaboration in addressing shared security concerns.
India’s “No to 9/11 Legacy” isn’t just a slogan; it’s a testament to our resilience. We remember the pain, the loss, and the unity that followed, but we also choose to move forward, to build a future where such tragedies are not repeated.
It’s a reminder of the powerful words, “Have you no sense of decency, sir, at long last?” have you no sense of decency sir – a plea for compassion and understanding that echoes through the ages. We stand united, not just against terrorism, but against any act that seeks to divide us.
This is the legacy of 9/11 in India: a commitment to peace, progress, and a shared humanity.
- The US-India Joint Strategic Vision for the 21st Century (2006):This vision document, signed by the leaders of both countries, underscored the shared interests and common values that underpinned the growing bilateral relationship. It reaffirmed the commitment to a strong strategic partnership and Artikeld a shared vision for a peaceful and prosperous Indo-Pacific region.
The “War on Terror” and India’s Foreign Policy
The US-led “war on terror” following 9/11 significantly influenced India’s foreign policy, pushing it to play a more active role on the global stage. The shared threat of terrorism and the need to counter the rise of extremist ideologies brought India and the US together in a common cause.
India’s refusal to endorse the “war on terror” narrative after 9/11, prioritizing diplomacy and independent foreign policy, remains a defining aspect of its international relations. This stance, coupled with its growing economic and military power, has undoubtedly contributed to the current escalation of tensions, as the US intensifies its war of words against China and its allies.
While the US seeks to isolate China, India’s independent approach, rooted in its 9/11 legacy, provides a unique perspective on global power dynamics.
This convergence of interests propelled India to become a more vocal and engaged player in global affairs, particularly in the context of international counterterrorism efforts.
- India’s Rise as a Counterterrorism Partner:The shared threat of terrorism prompted India to actively engage with the US and other international partners in counterterrorism initiatives. India strengthened its domestic counterterrorism capabilities and participated in joint intelligence sharing, training programs, and multilateral counterterrorism frameworks.
- India’s Growing Global Standing:India’s proactive role in the “war on terror” and its commitment to international counterterrorism efforts contributed to its growing global standing. The country emerged as a key partner in the fight against terrorism, enhancing its credibility and influence in the international arena.
Shared Security Interests and Cooperation
The shared threat of terrorism and the common goal of countering extremist ideologies fostered a deep sense of shared security interests between India and the US. This convergence of interests paved the way for enhanced cooperation in areas such as intelligence sharing, military exercises, and capacity building.
India’s “No to 9/11 Legacy” stance is a complex one, reflecting a deep-seated distrust of unchecked security measures. It’s a stance that resonates with the core message of Amnesty International’s recent report, amnesty international no shortcut to genuine security , which argues that genuine security cannot be achieved through shortcuts or the erosion of human rights.
India’s approach, while rooted in a desire for safety, must be carefully balanced against the fundamental principles of justice and human dignity.
The common threat of terrorism also served as a catalyst for a more robust dialogue and collaboration between the two countries, further strengthening their strategic partnership.
- Intelligence Sharing and Counterterrorism Cooperation:The 9/11 attacks underscored the need for close intelligence sharing and cooperation between India and the US. Both countries established mechanisms for intelligence exchange, joint operations, and capacity building programs to enhance their counterterrorism capabilities.
- Military Exercises and Joint Operations:India and the US have significantly increased the frequency and scope of joint military exercises since 9/11. These exercises, including the annual “Yudh Abhyas” and “Malabar” exercises, have enhanced interoperability and cooperation between the armed forces of both countries, bolstering their ability to respond to shared security challenges.
India’s Counterterrorism Efforts in the Post-9/11 Era
The 9/11 attacks were a watershed moment for India, prompting a significant shift in its counterterrorism strategy. The attacks highlighted the global nature of terrorism and the need for enhanced international cooperation to combat it. In response, India embarked on a multi-pronged approach, encompassing both domestic and international efforts to counter terrorism.
Domestic Counterterrorism Measures
India’s domestic counterterrorism measures have evolved significantly since 9/The government has strengthened its intelligence gathering capabilities, implemented stricter security measures, and enacted new legislation to combat terrorism. Key initiatives include:
- Establishment of the National Investigation Agency (NIA):The NIA was established in 2008 to investigate and prosecute terrorism-related offenses. It has played a crucial role in disrupting terrorist networks and bringing perpetrators to justice.
- Strengthening of Security Forces:India has significantly enhanced the capabilities of its security forces, including the Border Security Force (BSF), the Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF), and the National Security Guard (NSG). These forces have been equipped with modern weaponry and trained to counter terrorist threats.
- Anti-Terrorism Legislation:India has enacted several anti-terrorism laws, including the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA) and the Prevention of Terrorism Act (POTA). These laws provide legal frameworks for the investigation, prosecution, and punishment of terrorist activities.
- Counter-Radicalization Programs:The government has implemented counter-radicalization programs to address the root causes of terrorism, including poverty, social exclusion, and religious extremism. These programs aim to promote tolerance and understanding, and to counter the influence of extremist ideologies.
International Counterterrorism Cooperation
India has actively engaged in international counterterrorism cooperation since 9/Recognizing the transnational nature of terrorism, India has forged strategic partnerships with several countries, including the United States, Russia, and the United Kingdom. Key aspects of India’s international counterterrorism efforts include:
- Intelligence Sharing:India has established robust intelligence-sharing mechanisms with its partners, enabling the exchange of information on terrorist threats and activities. This collaboration has been crucial in disrupting terrorist plots and preventing attacks.
- Joint Counterterrorism Exercises:India participates in regular joint counterterrorism exercises with its partners, enhancing interoperability and coordination between security forces. These exercises provide valuable training and experience in dealing with terrorist threats.
- Multilateral Cooperation:India actively participates in multilateral counterterrorism initiatives, such as the United Nations Security Council’s Counter-Terrorism Committee (CTC) and the Global Counterterrorism Forum (GCTF). These platforms provide opportunities for India to share its expertise and contribute to the development of global counterterrorism strategies.
- Diplomatic Efforts:India has engaged in diplomatic efforts to isolate and pressure terrorist groups, seeking international condemnation and sanctions against them. This has been instrumental in curtailing the support networks and financial resources of terrorist organizations.
Comparison with Other Nations’ Counterterrorism Approaches
India’s counterterrorism approach shares similarities with other nations, such as the emphasis on intelligence gathering, security measures, and international cooperation. However, India’s approach is also characterized by certain unique challenges and perspectives.
- Internal Security Threats:India faces a complex internal security environment, with a history of separatist movements and ethno-religious conflicts. This has led to a focus on addressing internal security threats, alongside the fight against international terrorism.
- Cross-Border Terrorism:India has been a victim of cross-border terrorism emanating from neighboring countries, particularly Pakistan. This has necessitated a strong focus on border security and counter-infiltration measures.
- Cybersecurity Threats:India has faced increasing cyber threats from terrorist groups, who use the internet for propaganda, recruitment, and planning attacks. This has prompted a focus on cybersecurity measures and the development of capabilities to counter cyber terrorism.
Effectiveness of India’s Counterterrorism Efforts
India’s counterterrorism efforts have had a mixed record of success. While there have been significant achievements in disrupting terrorist plots and reducing the incidence of terrorist attacks, challenges remain.
- Successes:India has successfully disrupted numerous terrorist plots and arrested key operatives. The NIA has played a significant role in dismantling terrorist networks and bringing perpetrators to justice. Increased security measures have also deterred terrorist attacks.
- Challenges:Despite these successes, terrorism remains a persistent threat in India. Terrorist groups continue to operate in remote areas, and the internet provides them with new avenues for recruitment and propaganda. The challenge of cross-border terrorism also persists.
The Legacy of 9/11 on India’s Domestic Landscape
The 9/11 attacks had a profound and enduring impact on India’s domestic landscape, shaping its political discourse, media narratives, and social fabric. The attacks, which targeted the United States, a key strategic partner for India, sparked a heightened sense of insecurity and fueled a growing awareness of the global threat of terrorism.
The Rise of Nationalist Sentiment and Security Concerns
The 9/11 attacks, in the wake of the Kargil War, solidified India’s national security concerns and led to a resurgence of nationalist sentiment. The attacks demonstrated the vulnerability of even the most powerful nations to terrorism, prompting India to re-evaluate its own security posture and strengthen its counterterrorism capabilities.
This resulted in a significant increase in defense spending, the establishment of new security agencies, and a greater focus on intelligence gathering and border security. The attacks also led to a surge in public support for the government’s security policies, which further strengthened the position of nationalist parties and leaders.
The Influence of 9/11 on India’s Media Landscape
The 9/11 attacks had a significant impact on India’s media landscape, particularly in terms of the portrayal of terrorism and national security. The attacks led to a surge in media coverage of terrorism, with news channels and newspapers devoting considerable attention to the threat of terrorism, both domestically and internationally.
This heightened media focus on terrorism led to a more polarized public discourse on national security, with some arguing for stricter security measures and others expressing concerns about civil liberties.
The Impact of 9/11 on India’s Social Fabric, Indias no to 9 11 legacy
The 9/11 attacks had a complex and multifaceted impact on India’s social fabric, particularly in terms of the role of religion, identity, and community in the context of terrorism. The attacks, which were perpetrated by Islamic extremists, led to a rise in Islamophobia and anti-Muslim sentiment in some sections of Indian society.
This was exacerbated by the media’s portrayal of terrorism, which often focused on the religious and ideological motivations of the attackers.
India’s Role in the Global Counterterrorism Landscape
India has emerged as a significant player in the global counterterrorism landscape, actively engaging in international efforts to combat terrorism. The country’s long-standing experience with terrorism, coupled with its strategic location and growing global influence, has positioned India as a vital partner in the fight against this global threat.
India’s Contributions to International Counterterrorism Efforts
India’s contributions to international counterterrorism efforts are multifaceted, encompassing participation in global organizations, initiatives, and partnerships. India’s engagement in these platforms demonstrates its commitment to working collaboratively with the international community to address the challenges posed by terrorism.
- United Nations Security Council (UNSC):India has been a vocal advocate for strengthening the UN’s role in counterterrorism, pushing for comprehensive strategies that address the root causes of terrorism and promote international cooperation. As a non-permanent member of the UNSC, India has actively participated in the drafting and implementation of key resolutions on counterterrorism, including those focused on combating financing of terrorism, disrupting terrorist networks, and addressing the role of the internet in terrorism.
- Financial Action Task Force on Money Laundering (FATF):India is a founding member of the FATF, an intergovernmental organization that sets international standards for combating money laundering and terrorist financing. India has actively contributed to the development of FATF recommendations and has been instrumental in implementing these standards within its own financial system.
This commitment to financial transparency and accountability has been crucial in disrupting the financial networks used by terrorist organizations.
- Global Counterterrorism Forum (GCTF):India is a founding member of the GCTF, a platform for sharing best practices and promoting cooperation in counterterrorism. The GCTF provides a space for countries to collaborate on practical initiatives, such as countering terrorist propaganda, strengthening border security, and promoting community engagement in counterterrorism efforts.
India has actively participated in GCTF working groups and has contributed to the development of key initiatives, including the “GCTF Strategy to Counter Violent Extremism.”
India’s Role in Promoting International Cooperation Against Terrorism
India has played a key role in promoting international cooperation against terrorism through bilateral and multilateral partnerships. The country’s regional and global partnerships have been instrumental in building a network of cooperation to address the shared threat of terrorism.
- Regional Cooperation:India has been at the forefront of regional counterterrorism efforts, working closely with its neighbors to address the common challenges posed by terrorism. The “Heart of Asia – Istanbul Process” is a prominent example of India’s commitment to regional cooperation, providing a platform for dialogue and cooperation on counterterrorism and security issues.
India has also actively engaged in bilateral counterterrorism cooperation with countries in its immediate neighborhood, including Bangladesh, Bhutan, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. These partnerships have focused on sharing intelligence, capacity building, and joint operations to combat terrorism.
- Global Partnerships:India has also forged strong counterterrorism partnerships with key global players, including the United States, Russia, France, and the United Kingdom. These partnerships have been instrumental in sharing intelligence, coordinating counterterrorism operations, and developing joint strategies to address the evolving threat of terrorism.
India’s participation in the “Quadrilateral Security Dialogue” (QUAD), a strategic partnership with the US, Japan, and Australia, further underscores its commitment to working with like-minded partners to counter terrorism and promote security in the Indo-Pacific region.
India’s Key Counterterrorism Initiatives and Partnerships
| Initiative/Partnership | Objective | Impact ||—|—|—|| National Counterterrorism Centre (NCTC)| To coordinate and enhance intelligence sharing among various security agencies within India. | Improved intelligence gathering and analysis, leading to more effective counterterrorism operations. || National Investigation Agency (NIA)| To investigate and prosecute terrorism-related offenses in India.
| Strengthened law enforcement capabilities and increased convictions in terrorism cases. || India-US Counterterrorism Cooperation Framework| To enhance cooperation in areas such as intelligence sharing, capacity building, and joint training. | Improved information sharing and coordination in counterterrorism efforts, leading to more effective operations.
|| India-France Counterterrorism Partnership| To strengthen cooperation in counterterrorism training, technology sharing, and joint exercises. | Enhanced capabilities in counterterrorism training and technology, contributing to improved preparedness and response. || India-Russia Counterterrorism Cooperation| To promote cooperation in areas such as intelligence sharing, capacity building, and joint exercises.
| Strengthened counterterrorism cooperation, including joint training and exercises, contributing to improved preparedness and response. |