Afghanistan: Time of Transition
Afghanistan time of transition – Afghanistan: Time of Transition is a phrase that captures the complex and dynamic state of the country as it navigates a path towards a more stable and prosperous future. After decades of conflict and political turmoil, Afghanistan is facing a multitude of challenges, from rebuilding its infrastructure and economy to fostering social harmony and ensuring security.
The nation’s history is marked by foreign intervention, internal power struggles, and a deeply ingrained cultural fabric that has been shaped by these events.
This period of transition is characterized by a delicate balance of hope and uncertainty. The international community is closely watching as Afghanistan attempts to forge a new identity, while grappling with the legacy of the past. This exploration will delve into the key factors that are shaping Afghanistan’s present and future, examining the historical context, political landscape, economic situation, social dynamics, security challenges, and international relations that are intertwined in this critical juncture.
Historical Context

Afghanistan’s current state is the culmination of a long and tumultuous history marked by foreign interventions, internal conflicts, and political instability. Understanding the historical events that have shaped the country is crucial for comprehending its present challenges and potential pathways to a more peaceful and prosperous future.
The Role of Foreign Powers in Afghanistan’s History
Foreign powers have played a significant role in Afghanistan’s history, often contributing to instability and exacerbating existing conflicts. The country’s strategic location at the crossroads of Central Asia, South Asia, and the Middle East has made it a target for empires and nations seeking to control trade routes and influence regional power dynamics.
- The British Empire:The British Empire’s involvement in Afghanistan dates back to the 19th century, with the First Anglo-Afghan War (1838-1842) and the Second Anglo-Afghan War (1878-1880). These conflicts were driven by British interests in securing its colonial possessions in India and controlling the trade routes to Central Asia.
- The Soviet Union:The Soviet Union invaded Afghanistan in 1979, sparking a protracted war that lasted for a decade. The Soviet intervention aimed to prop up a pro-Soviet government and prevent the spread of Islamic fundamentalism in the region. The war resulted in the deaths of hundreds of thousands of Afghans and the displacement of millions more.
- The United States:The United States intervened in Afghanistan following the 9/11 terrorist attacks, launching a military campaign to dismantle al-Qaeda and remove the Taliban regime from power. The US involvement has continued for over two decades, leading to a significant increase in military spending and the deaths of thousands of Afghan civilians.
Different Political Systems in Afghanistan
Afghanistan has experienced a variety of political systems throughout its history, ranging from monarchies to republics to theocratic regimes.
- The Monarchy (1747-1973):The Durrani dynasty established a powerful monarchy in the 18th century, uniting most of the Afghan territory under a single ruler. The monarchy was characterized by centralized power, a strong military, and a complex system of patronage.
- The Republic (1973-1978):A republic was declared in 1973 after a coup d’état led by Mohammad Daoud Khan, who overthrew the monarchy. The republic was short-lived, however, as Daoud Khan was overthrown by a communist coup in 1978.
- The Communist Regime (1978-1992):The communist regime, led by the People’s Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA), came to power in 1978 after a series of coups. The regime’s policies were highly unpopular, leading to widespread resistance and the Soviet invasion in 1979.
- The Taliban Regime (1996-2001):The Taliban, a fundamentalist Islamic group, emerged from the chaos of the Soviet withdrawal and captured Kabul in 1996. The Taliban imposed a strict interpretation of Islamic law, banning women from education and employment, and severely restricting personal freedoms.
- The Islamic Republic of Afghanistan (2001-present):The Islamic Republic of Afghanistan was established after the US-led invasion in 2001. The new government, backed by the international community, implemented a new constitution, held democratic elections, and sought to rebuild the country.
Current Political Landscape
Afghanistan’s current political landscape is a complex and evolving one, shaped by decades of conflict, foreign intervention, and internal power struggles. Following the withdrawal of US forces and the Taliban’s takeover in August 2021, the country is facing a multitude of challenges, including a fragile political system, economic instability, and humanitarian crisis.
The Current Political Structure
The Taliban, now in control of Afghanistan, has established an interim government, with a supreme leader, a council of ministers, and a number of provincial governors. However, the legitimacy and recognition of this government remain highly contested. Many countries, including the United States and its allies, have refused to recognize the Taliban government, citing concerns about its human rights record and its lack of inclusivity.
Challenges Facing the Current Government
The Taliban government faces a number of significant challenges:* International Isolation:The lack of international recognition has severely limited the Taliban’s access to foreign aid and financial resources, which are crucial for rebuilding the country’s economy and providing basic services to its people.
Economic Crisis
Afghanistan’s economy has been devastated by years of war and the collapse of the previous government. The Taliban government is struggling to provide essential services, including healthcare, education, and electricity.
Humanitarian Crisis
Afghanistan’s transition is a complex journey, marked by challenges on multiple fronts. One of the most pressing issues is the economic situation, with the country facing a dire humanitarian crisis. The scale of the debt crisis, as outlined in this insightful article the scale of the debt crisis , adds another layer of complexity to the already challenging environment.
Navigating this economic landscape will be crucial for Afghanistan’s future stability and progress.
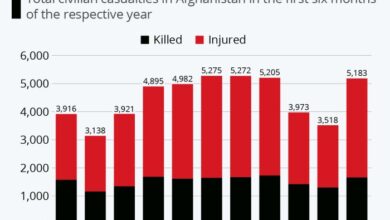
The humanitarian situation in Afghanistan is dire, with millions of people facing food insecurity, displacement, and lack of access to healthcare. The Taliban government is struggling to cope with the crisis, and the international community has been slow to provide adequate assistance.
Security Concerns
The Taliban faces a number of security threats, including the Islamic State Khorasan Province (ISKP), which is actively operating in the country. There are also concerns about the potential for resurgence of armed resistance groups.
Social and Cultural Issues
The Taliban government’s strict interpretation of Islamic law has led to concerns about the rights of women and minorities. The Taliban has imposed restrictions on women’s education and employment, and there have been reports of human rights abuses against minorities.
Role of Different Political Factions
The Afghan political landscape is characterized by a number of different political factions, each with its own interests and objectives:* The Taliban:The Taliban is the dominant political force in Afghanistan, controlling the government and most of the country’s territory. Its objectives include establishing an Islamic state based on its interpretation of Sharia law, and restoring peace and security.
The National Resistance Front (NRF)
The NRF is a coalition of anti-Taliban forces, led by Ahmad Massoud, the son of the late anti-Taliban commander Ahmad Shah Massoud. The NRF is active in the Panjshir Valley and other parts of the country, and its objective is to overthrow the Taliban government.
Other Political Groups
There are a number of other political groups operating in Afghanistan, including the Hizb-e Islami, the Jamiat-e Islami, and the Junbish-e Milli. These groups have varying degrees of influence and support, and their objectives range from seeking power to advocating for specific policies.
Economic Situation
Afghanistan’s economic landscape has been profoundly shaped by decades of conflict, political instability, and a reliance on foreign aid. Despite recent efforts to rebuild and develop, the country faces significant economic challenges.
Impact of War on the Afghan Economy
The prolonged conflict has had a devastating impact on Afghanistan’s economy. The war has destroyed infrastructure, disrupted agricultural production, and hampered economic activity. The country has been heavily reliant on foreign aid, which has accounted for a substantial portion of government revenue and development spending.
However, the withdrawal of international forces and the subsequent reduction in aid have created a significant economic crisis.
Afghanistan’s time of transition is a stark reminder of the complex challenges facing nations in flux. The potential for instability, even violence, is a real concern, as we’ve seen in other regions like the Korean Peninsula, where the ongoing nuclear standoff with North Korea north korea and nuclear weapons continues to raise global anxieties.
While Afghanistan’s future is uncertain, lessons learned from other transitions can help guide its path towards a more stable and prosperous future.
Economic Challenges Facing Afghanistan
- High Poverty Rates:Afghanistan has one of the highest poverty rates in the world, with a significant portion of the population living below the poverty line. This is due to factors such as limited access to education and healthcare, lack of employment opportunities, and ongoing conflict.
- Limited Infrastructure:The country’s infrastructure, including roads, electricity, and communication networks, remains underdeveloped, hindering economic growth and development.
- Dependence on Foreign Aid:Afghanistan’s economy is heavily reliant on foreign aid, which has been a major source of revenue and development funding. The withdrawal of international forces and the subsequent reduction in aid have created a significant economic crisis.
- Corruption:Corruption is a major obstacle to economic development in Afghanistan. It undermines good governance, discourages investment, and hinders the efficient allocation of resources.
- Lack of Diversification:The Afghan economy is largely dependent on agriculture, which is vulnerable to drought and other natural disasters. There is a need for diversification into other sectors, such as manufacturing and services, to promote sustainable economic growth.
Potential for Economic Growth and Development
Despite the challenges, Afghanistan has the potential for economic growth and development. The country is rich in natural resources, including minerals, hydropower, and agricultural land. With a focus on good governance, infrastructure development, and investment in human capital, Afghanistan can create a more prosperous future.
“The Afghan economy has the potential to grow and develop, but it needs to address the challenges of poverty, corruption, and lack of infrastructure.”
Social and Cultural Dynamics
Afghanistan’s social and cultural landscape is deeply rooted in its rich history and traditions, shaped by centuries of interaction with diverse civilizations. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for comprehending the country’s current transition and its future.
Impact of Conflict on Afghan Society
The decades-long conflict in Afghanistan have had a profound impact on its social fabric. The violence has displaced millions, disrupted education and healthcare systems, and led to widespread poverty. The conflict has also contributed to the erosion of social trust, increased polarization, and undermined traditional social structures.
The trauma experienced by many Afghans, particularly women and children, has long-lasting consequences for their mental and physical well-being.
The Role of Women in Afghan Society
The role of women in Afghan society is a complex and evolving issue. While Afghan culture traditionally places a high value on family and community, women have faced significant challenges in accessing education, healthcare, and economic opportunities. The conflict has further exacerbated these challenges, limiting women’s mobility and increasing their vulnerability to violence.
However, there is growing recognition of the importance of women’s participation in all aspects of Afghan life.
“Women are the backbone of Afghan society, and their empowerment is essential for the country’s future.”
The Afghan government and international organizations are working to promote women’s rights and ensure their equal participation in education, politics, and the economy.
Social and Cultural Values
Afghan society is characterized by strong family ties, a deep respect for elders, and a strong sense of community. Hospitality is a core value, and guests are welcomed with warmth and generosity. Islam plays a central role in Afghan life, influencing many aspects of social customs, dress, and daily routines.
Afghanistan is in a time of transition, grappling with the aftermath of a tumultuous period. The country’s history is intertwined with the larger complexities of the Middle East, a region with a long history of conflict. To understand the current situation in Afghanistan, it’s essential to delve into the historical context of the Middle East, which is intricately linked to the the middle east conflict a brief background.
This understanding provides a crucial lens through which to analyze the challenges Afghanistan faces in its journey toward stability and peace.
- Family Ties:Extended families are the cornerstone of Afghan society, and family members often live together in close proximity. Family honor is paramount, and individuals are expected to act in ways that bring credit to their family.
- Respect for Elders:Older generations are highly respected, and their wisdom and experience are valued. Children are expected to show deference to their elders and follow their guidance.
- Community Spirit:Afghans have a strong sense of community, and neighbors often support each other in times of need. This spirit of solidarity has been particularly important during times of conflict and hardship.
- Hospitality:Hospitality is a cornerstone of Afghan culture, and guests are always welcomed with warmth and generosity. Even strangers are treated with kindness and respect.
Security and Stability
Afghanistan’s security situation remains volatile and complex, posing significant challenges to the country’s transition. The withdrawal of US and NATO forces in 2021 marked a significant shift in the security landscape, leaving the country vulnerable to various threats.
The Security Situation
The Taliban’s takeover in August 2021 ushered in a new era of governance, with the group attempting to consolidate its control over the country. However, the group faces ongoing resistance from various factions, including the National Resistance Front (NRF), a group led by Ahmad Massoud, son of the late Ahmad Shah Massoud, a prominent anti-Taliban figure.
The NRF operates primarily in the Panjshir Valley, a strategically important region north of Kabul.
Challenges to Maintaining Peace and Stability
Maintaining peace and stability in Afghanistan presents numerous challenges:* Ongoing Insurgency:The Taliban’s grip on power is not absolute, and several groups continue to oppose their rule. The NRF remains active in the Panjshir Valley, while other armed groups, including ISIS-K, operate in various parts of the country.
Regional Instability
Afghanistan’s borders with Pakistan and Iran are porous, allowing for the movement of militants and weapons. The instability in neighboring countries, such as Pakistan, also contributes to the security challenges faced by Afghanistan.
Economic Crisis
The collapse of the Afghan economy has exacerbated poverty and unemployment, creating a fertile ground for recruitment by insurgent groups. The economic crisis has also weakened the government’s ability to provide basic services and maintain security.
Humanitarian Crisis
The ongoing humanitarian crisis in Afghanistan has displaced millions of people and created a significant strain on the country’s resources. The crisis has also weakened the government’s ability to provide security and maintain order.
Key Actors in the Security Landscape, Afghanistan time of transition
The following are some of the key actors involved in the security landscape of Afghanistan:* The Taliban:The Taliban is the de facto governing body of Afghanistan. The group controls most of the country and is responsible for maintaining security.
National Resistance Front (NRF)
The NRF is a group led by Ahmad Massoud that opposes the Taliban. The group operates primarily in the Panjshir Valley and has been involved in clashes with the Taliban.
ISIS-K
ISIS-K is a branch of the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria that operates in Afghanistan. The group has been responsible for several high-profile attacks, including the bombing at Kabul airport in August 2021.
International Community
The international community, including the United Nations, the European Union, and various countries, plays a role in Afghanistan’s security landscape. These organizations provide humanitarian assistance and support to the Afghan government and people.
Regional Powers
Regional powers, such as Pakistan, Iran, and Russia, have a vested interest in Afghanistan’s stability. These countries have been involved in efforts to influence the Afghan government and promote their own interests.
International Relations: Afghanistan Time Of Transition

Afghanistan’s international relations are a complex web of political, economic, and security interests, shaped by decades of conflict and instability. International actors have played a significant role in the country’s history, from the Soviet invasion in the 1980s to the US-led intervention after 9/11.
Today, Afghanistan continues to rely heavily on international support for its reconstruction and development.
Role of International Actors
The international community has been deeply involved in Afghanistan since the fall of the Taliban regime in 2001. A wide range of actors, including the United Nations, the European Union, regional powers like India and Pakistan, and individual countries, have contributed to the country’s political, economic, and social development.
Key International Actors and Their Roles
- United Nations:The UN has played a crucial role in facilitating peace negotiations, providing humanitarian assistance, and supporting the Afghan government in its efforts to rebuild the country. The UN Assistance Mission in Afghanistan (UNAMA) monitors the human rights situation and supports the Afghan government in its efforts to rebuild the country.
- NATO:NATO led the International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) in Afghanistan from 2001 to 2014, providing security and training to Afghan forces. After the withdrawal of ISAF, NATO transitioned to a training and advisory role through the Resolute Support Mission.
- United States:The US has been the largest contributor to Afghanistan’s reconstruction efforts, providing billions of dollars in aid and playing a significant role in military operations. However, the US withdrawal in 2021 left a void in the country’s security and stability.
- European Union:The EU has been a major donor to Afghanistan, providing financial and technical assistance for development projects. The EU also plays a role in promoting human rights and democracy in the country.
- Regional Powers:Regional powers such as India, Pakistan, Iran, and Russia have also played significant roles in Afghanistan’s affairs. Their interests in the country are often intertwined with their regional geopolitical ambitions and security concerns.
Impact of Foreign Aid
Foreign aid has been a crucial lifeline for Afghanistan’s economy, providing essential support for infrastructure development, education, healthcare, and other vital sectors. However, the impact of foreign aid has been mixed.
Positive Impacts
- Economic Development:Foreign aid has helped to rebuild Afghanistan’s infrastructure, improve its economy, and create jobs. The country has seen significant progress in areas like education, healthcare, and agriculture.
- Humanitarian Assistance:Foreign aid has been vital in providing humanitarian assistance to Afghan people, particularly in times of crisis. Aid organizations have played a crucial role in delivering food, water, shelter, and medical supplies to those in need.
- Support for the Government:Foreign aid has helped to sustain the Afghan government, providing financial support for its operations and services.
Negative Impacts
- Dependency:Heavy reliance on foreign aid has created a culture of dependency in Afghanistan, making it difficult for the country to become self-sufficient.
- Corruption:Corruption has been a major problem in Afghanistan, with aid funds often being misused or diverted. This has undermined the effectiveness of aid and eroded public trust.
- Lack of Sustainability:Many aid projects have lacked sustainability, with funding often drying up after the initial phase. This has led to incomplete projects and a lack of long-term impact.
Different Approaches of Different Countries
Different countries have taken different approaches towards Afghanistan, reflecting their unique interests and priorities.
Comparing and Contrasting Approaches
| Country | Approach | Key Priorities |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Military intervention, counterterrorism, nation-building | Combating terrorism, promoting democracy, supporting Afghan security forces |
| Russia | Pragmatic engagement, maintaining regional influence, counterbalancing US influence | Securing its borders, preventing instability, supporting its allies |
| China | Economic diplomacy, infrastructure development, strategic partnership | Securing access to resources, expanding trade, promoting regional stability |
| India | Development assistance, cultural ties, strategic partnership | Strengthening ties with Afghanistan, promoting regional stability, countering Pakistani influence |
| Pakistan | Complex relationship, supporting Afghan peace process, maintaining influence | Securing its border, preventing instability, promoting its interests in Afghanistan |
Challenges and Opportunities

Afghanistan’s transition is a complex and multifaceted process, marked by both significant challenges and opportunities for progress. While the country grapples with the legacy of conflict, political instability, and economic hardship, there are also potential avenues for development and a more stable future.
Challenges Facing Afghanistan
The challenges facing Afghanistan are deeply intertwined and multifaceted. The country’s long history of conflict has left it with a fragile infrastructure, a weak economy, and a deeply divided society. These challenges are further exacerbated by the ongoing political instability, the pervasive corruption, and the threat of terrorism.
- Political Instability:The current political landscape is characterized by a lack of consensus and a power struggle among various factions. This instability makes it difficult to implement effective policies and fosters a climate of uncertainty and fear.
- Economic Hardship:Afghanistan has one of the poorest economies in the world, with a high level of poverty and unemployment. The country relies heavily on foreign aid, which is often subject to political fluctuations.
- Security and Stability:The ongoing threat of terrorism and insurgency remains a major challenge to Afghanistan’s stability. The Taliban’s presence in many parts of the country continues to pose a serious security threat.
- Social and Cultural Dynamics:Afghanistan’s society is deeply divided along ethnic, tribal, and religious lines. These divisions have often been exploited by political actors to further their own interests.
- Corruption:Widespread corruption at all levels of government has undermined trust in the state and hindered development efforts. It has also created a climate of impunity for those who abuse their power.
- Humanitarian Crisis:Afghanistan is facing a severe humanitarian crisis, with millions of people in need of food, water, and shelter. The ongoing conflict and the economic downturn have exacerbated the situation.
Opportunities for Progress and Development
Despite the many challenges, Afghanistan also has significant opportunities for progress and development. The country has a young and growing population, abundant natural resources, and a strategic location. These factors, coupled with the international community’s continued support, offer a path towards a more stable and prosperous future.
- Economic Development:Afghanistan has a significant potential for economic growth, particularly in the areas of agriculture, mining, and energy. The country’s strategic location could also make it a hub for regional trade.
- Infrastructure Development:Investing in infrastructure, such as roads, railways, and power plants, is crucial for economic growth and development. It can create jobs, improve access to markets, and enhance connectivity.
- Education and Healthcare:Investing in education and healthcare is essential for human development and economic progress. It can empower individuals, improve health outcomes, and create a more skilled workforce.
- Peace and Reconciliation:Achieving a lasting peace and reconciliation is crucial for Afghanistan’s stability and development. It requires dialogue and compromise among all stakeholders, including the government, the Taliban, and other armed groups.
- Good Governance:Establishing a transparent, accountable, and effective government is essential for good governance and development. This requires strengthening institutions, fighting corruption, and promoting the rule of law.